Topic 5 Flashcards
(24 cards)
What is the difference between an exothermic and an endothermic reaction? (2 marks)
An exothermic reaction gives out heat during the reaction, shown by a rise in temperature in the surroundings
An endothermic reaction takes in heat during the reaction, shown by a decrease in the surrounding temperature
Give 3 examples of exothermic reactions (3 marks)
Some hand warmers use the exothermic oxidation of iron in the air
Self-heating cans of chocolate or coffee
Burning of fuels (combustion)
Describe an endothermic reaction (2 marks)
Heating calcium carbonate causes the calcium carbonate to decompose into calcium oxide (also known as quicklime) and carbon dioxide
What is the law of conversation of energy? (2 marks)
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only moved or transferred
A student prepares a flask containing ethanoic acid and measures its temperautre as 22.5 °C. He then adds dilute potassium hydroxide solution which is 21 °C. After 2 minutes the temperature of the reaction mixture is 28.5 °C. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? (1 mark)
Exothermic because the temperature of the mixture is lower than it was beforehand
How do you measure the amount of energy released by a chemical reaction? (2 marks)
Take the temperature of the reagents and mix them in a polystyrene cup and measure the temperature of the solution at the end of the reaction
What two methods could you use to reduce energy loss during energy measurements? (2 marks)
By putting the polystyrene cup into a beaker of coton wool to give more insulation
By putting a lid on the cup to reduce energy lost by evaporation
How could you test the effect of acid concentration on the energy released in a neutralisation reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide? (5 marks)
- Put 25cm3 of 0.25mol/dm3 of hyldrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide in separate beakers
- Place the breakers in a water bath set to 25 °C until they are both at the same temperature (25 °C)
- Add the HCl followed by the NaOH to a polystyrene cup with a lid
- Take the temperature of the mixture every 30 seconds, and record the highest temperature
- Repeat steps 1-4 using 0.5moll/dm3 and then 1mol/dm3 of hydrochloric acid
What is activation energy? (1 mark)
The initial rise in energy representing the energy needed to start the reaction, resulting in a chemical reaction
Which is exothermic and which is endothermic? (2 marks)
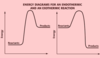
Left is endothermic
Right is exothermic
True or false: during a chemical reaction, old bonds are broken and new bonds are formed (1 mark)
True
Fill in the blanks.
Energy must be _____ to break existing bonds - so bond breaking is _____
Energy is _____ when new bonds are formed - so bond formation is _____.
Supplied, endothermic, released, exothermic
How can you calculate overall energy change? (2 marks)
Using known bond energies
What is the overall energy change? (1 mark)
The sum of the energies needed to break bonds in the reactants minus the energy released when the new bonds are formed in the prodcuts
N2 reacts with H2 in the following reaction: N2 + 3H2 = 2NH3
The bond energies for these molecules are:
N_=_N: 1941 kJ/mol; H-H: 436 kJ/mol; N-H: 391 kJ/mol
Calculate the overall energy change for this reaction (3 marks)
H H
N_=_N + 3H-H ⇒ N + N
H H H H
Energy required to break original bonds:
(1 x N_=_N) + (3 x H-H) = 941 kJ/mol + 1308 kJ/mol = 2249 kJ/mol
Energy released by forming new bons:
(6 x N-H) = 2346 kJ/mol
Overall energy change:
2249 kJ/mol - 2346 kJ/mpl = -97kJ/mol
What is an electrochemical cell? (1 mark)
An electrochemical cell is a basic system made up of two diferent electrodes in contact with an electrolyte
What is electrolyte? (1 mark)
A liquid that contains ions which react with the electrode
Name 3 factors that can affect the voltage of a cell (3 marks)
The type of electrodes used
The difference in reactivity of the electrodes
The electrolyte used since different ions in soltuion will react differently with the metal electrodes used
How do non-rechargable batteries work? (3 marks)
They contain irreversible reactions that use up the reactants used in the cells. This means that once a reactant is used up, it can’t be reused and the reaction can’t happen anymore
The voltages of three cells, where one electrode is zinc and the other electrode changes each time are shown below. Zinc is less reactive than the other metals. Write the order of reactively of the metals used from lowest highest. Explain your answer (3 marks)
Metal 1: 4
Metal 2: 2.5
Metal 3: 3
Metal 2, metal 3, metal 1. Zinc is less reactive than all 3 metals, so the most reactive metal will make the cell with the greatest voltage, since there will be the biggest difference in reactivity. So the order of reactivity is simply the other of the size of the voltage
What happens when the fuel of a fuel cell enters the cell? Give an example (2 marks)
The cell becomes oxidised and sets up a potential difference within the cell. For example, the hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell combines both hydrogen and oxygen (shocking!) to produce nice clean water and release energy
In a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell, what happens when the oxygen and the hydrogen get inside? (3 marks)
- Hydrogen goes into the anode (-ve) and the oxygen goes into the cathode (+ve)
- The hydrogen loses electrons to produce H+ ions in a oxidation reaction
- The H+ ions in the electrolyte then move to the cathode
- At the cathode, oxygen gains electrons from the cathode and reacts with H+ ions to make water in a reduction reaction
- The electrons flow through an external circuit from the anode to the cathode - this is the electric current
The overall reaction is the hydrogen plus oxygen to make water
Give three reasons why fuel cell vehicles could be better than electric/battery powered vehicles (3 marks)
Fuel cells vehicles don’t produce as many pollutants as other fuels - no greenhouse gases, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide or carbon monoxide. The only by-products are water and heat. Whereas, electric vehciles have much more polluting batteries to dispose of when they aren’t needed anymore
Batteries in electric vehicles are rechargable only to a certain number of recharges, and are more expensive. This is not the case with fuel cell vehicles
Batteries also store less energy than fuel cells and so would need to be recharged more often, which could take a long time
Write the half-equation for the reaction of oxgen in a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell (2 marks)
At the anode:
H2 ⇒ 2H+ + 2e-
At the cathode:
O2 + 4H+ + 4e-⇒ 2H2O


