Tutorial - Hernias Flashcards
(36 cards)
Define hernia
A weakness in the abdominal wall where an internal organ/fatty tissue protrudes through
Below what line do you lose the posterior rectus sheath? What is the significance of losing the sheath?
Arcuate line Weakness below this line
What is the arcuate line?
A horizontal line between the umbilicus and pubic symphysis that demonstrates the end of the posterior rectus sheath
What are the common types of hernias?
Inguinal Femoral Para-umbilical Umbilical Epigastric
What kind of incision is shown?

Rooftop incision
What kind of incision is shown?
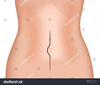
Midline
What is incision 1 known as?

Kocher incision
What kind of incision is commonly used for upper GI surgeries?
Rooftop incisions, e.g. gastrectomy, oesophagectomy
What kind of incision is used for an open colectomy?
Kocher
What type of hernias are there?
Primary
Incisional
What is an incisional hernia?
A hernia that occurs through a previously made incision in the abdominal wall
What are RFs for primary hernias?
Increased abdominal pressure
Obesity
What are RFs for incisional hernias?
Poor wound healing (e.g. DM, smoking, wound infection, steroids)
Technical problems, e.g. wrong sutures used
What are symptoms of hernias?
Swelling + pain most common
Obstruction (if small bowel in hernia)
Reducible
Can become incarcerated/strangulated
When are hernia swellings more noticible?
When you are standing up, better when lying
On coughing/increased intra-abdominal pressure
What signs might you see in an incarcerated hernia?
Tachycardia due to pain
What signs might you see in a strangulated hernia?
Pyrexia, tachycardia, skin changes e.g. cellulitis
How do you investigate a hernia?
Clinical diagnosis
For more complex hernias may do CT to see contents of hernia
How are hernias managed?
Surgical repair
What does surgical repair of a hernia involve?
Suturing defect back together
Inserting mesh to prevent recurrence
What are the risks of inserting mesh into a patient during hernia repair?
Infection (if bowel strangulated do not insert mesh as necrotic bowel puts risk of infection v. high)
Mesh rejection
Adhesions
What are risks of hernia repair operations?
Adhesions
Infections
Seroma
What are seromas?
A pocket of serous fluid that sometimes develops after surgery
How are seromas avoided?
Drains inserted


