UE fractures- pictures Flashcards
(44 cards)
The following shows which type of x-ray view in evaluation of which type of fx?
45 degree Cephalic tilt view
useful in evaluation of clavicle fx
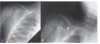
The following shows indication of what?

Surgical management of clavicular fx
(this shows tenting of the skin)
What is concerning about this x-ray image?

The fracture involves the distal 1/3, which is concerning. This fx requires surgical repair
What is the following X-ray showing?

This is a pathological fracture of the midshaft of the humerus.
The pic on the left shows a unicameral cyst (a weakened area of bone), which is how a midshaft fx is caused by FOOSH)

What type of fx is this and how would it be treated?

Midshaft humerus fracture
tx w/ surgery

What do the letters on the bottom pictures correspond to?

Letters= pediatric ossification centers
(#= age at which ossification center appears)
C- Capitellum (1)
R- Radial head (3)
I- Internal (medial) epicondyle (5)
T- Trochlea (7)
O- Olecranon (9)
E- External (lateral) epicondyle (11)- this is L in the picture
“CRITOE”
What does the following picture show?

Forearm compartment syndrome–> Volkmann’s Ischemia/contracture
(there will be pain w/ passive extension of the fingers)
What type of fracture? What is the Garland Classification of each?

Supracondylar fracture
A= Type I
B= Type II
C= Type III

What type of fracture and what is the Garland Classification

Supracondylar fracture
Type II
What type of fx and what is the Garland Classification?

Supracondylar fracture
Type I
What type of fx and what is the Garland Classification? What does this type of fracture mimic?

Supracondylar fracture
Type III
Mimics a posterior elbow dislocation

What type of fracture?
What is the management?

Supracondylar fracture

Non-surgical- Type I, Type II w/ reduction
Surgical- Type III, (Type II when reduction fails)
What type of fracture?
What “sign” is seen on this x-ray?
Other than AP and Lateral X-ray views, what other view should be obtained?

- Radial head fracture
- may be occult on initial x-rays–> look for fat pad sign
- Should also obtain oblique view

What type of fracture?

Radial head fracture
What type of fracture?
Stable or unstable?

Nightstick fracture (mid to distal ulnar shaft fracture)
Stable forearm fracture
What type of fracture?
Stable or unstable?

Both bone forearm fracture (radial and ulnar shaft fracture)
Unstable forearm fracture
What fracture? Stable or unstable? Management?

Monteggia fracture (ulna fx, radial head dislocation)
Unstable forearm fracture
Management- sx
What fracture? Stable or unstable? Management?

Galeazzi fracture (radius fx + carpoulnar dislocation)
Unstable forearm fracture
Management- Surgical
The following picture shows 2 different MOIs. Which fractures are associated w/ each?
What classic deformity is seen w/ each?

Left= Colle’s fracture (FOOSH w/ extension)–> dinner fork deformity
Right= Smith’s fracture (FOOSH w/ flexion)–> garden spade deformity

Which type of fracture is associated with the following deformity?

Colle’s fracture–> dinner fork deformity
Which type of fracture is associated with the following deformity?

Smith’s fracture–> Garden spade deformity
What type of fracture?
What other x-ray view should be obtained (other than AP and lateral)?

Colle’s fracture- dinner fork deformity
Should also obtain oblique view

What type of fracture?
What other x-ray view should be obtained (other than AP and lateral)?

Smith’s fracture (soft tissue swelling is unique to this)
Should obtain oblique view

What type of fracture? What population is this MC in?

Pediatric distal radial fracture–>
Radial torus (“Buckle”) fracture
MC in children <10


























