Unit 4 Flashcards
(63 cards)
Article I, Section 8
The section of the Constitution that lists the powers of Congress & the national government (Called Enumerated Powers).
U.S. House of Reps
435 Member chamber with each state having a different number of seats according to population. Majority controls all votes, all spending and taxing bills must originate there and all bills must also be passed by the Senate.
Reapportionment
The process of redrawing congressional district lines after the census determines how many districts each state gets.
Gerrymandering
The drawing of House district lines to give an advantage to one political party over another. This is usually done by compressing or diluting the opposition’s votes in various districts.
U.S. Senate
Consists of 100 members (2 from each state), members serve 6 year terms with 1/3 of the senate up for reelection every 2 years, complex rules, approves treaties & presidential appointments, Bills passed by the house must also be passed by the senate.
Advise and Consent
The power of the Senate to approve of presidential appointments and treaties.
Filibuster
The use of unlimited debate by one member of the Senate to “run out the clock” on legislation, which kills the bill.
Cloture
A vote of 60+ Senators to force someone to stop filibustering a bill.
•
Speaker of the House
Oversees the entire House and has a lot of influence over committee appointments and the fate of legislation. Elected by a simple majority of the House.
House Majority/Minority Leaders
House political party leader who maintains party loyalty by members of congress. Elected by majority of party members in both House & Senate.
Party Whips
Party “henchmen” that do the dirty-work of their political party to make sure that members vote the right way.
President of the Senate
(Vice President)
Presides over the Senate but has very little authority to enforce parliamentary matters or anything else. Can only vote to break a tie.
Senate Majority Leader
Has the real power in the Senate, makes committee appointments and decides when or how legislation will get heard.
President Pro-Tempore
Most senior member of the Senate, mostly an honorary position but is behind the Speaker of the House in the Presidential progression.
Standing Committee
Permanent committee in Congress that specializes in certain topic areas. Almost all bills must pass out of a committee before they can be voted on by the entire house.
Conference Committee
Temporary Committee composed of members of both the House and Senate to resolve differences between the House and Senate versions of a bill.
Sub-Committee
Committee that is more specialized than a standing committee
Rules Committee
House Only
Powerful committee that establishes when and under what terms a bill can be debated.
Appropriations Committee
House and Senate
very powerful standing committee in Congress that oversees all government spending
Ways & Means Committee
House only
A very powerful standing committee in Congress that oversees all federal government taxes and revenue.
Pork Barrel Legislation
Often unnecessary or impractical projects or tax loopholes obtained by a member of Congress. Very often, these projects are unnecessary. The projects or tax loopholes can then be exchanged for votes or campaign donations.
Law Making Process
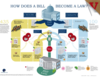
Logrolling
An arrangement between lawmakers to support each other’s legislation or pork barrel funding requests. Often, members will get their bills passed or projects funded by exchanging promises to vote for each other’s bills.
Article II
establishes the powers and responsibilities of the President & Bureaucracy (called the executive branch). The main function of the executive is to implement and enforce laws passed by Congress.


