Upper Limb Flashcards
(291 cards)
Notes on interosseous, palmar
unipennate muscles; remember PAD & DAB: Palmar interossei ADduct and Dorsal interossei ABduct, and you will be able to figure out where they must insert (Latin, inter = between + os = bone)


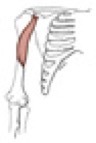
Notes on brachialis
a powerful flexor
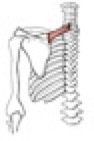
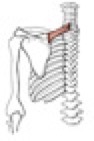
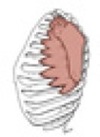
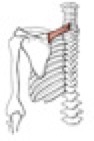
Action of serratus anterior
it draws the scapula forward; the inferior fibers rotate the scapula superiorly
Subclavius
Origin
Insertion

first rib and its cartilage
inferior surface of the clavicle

Large muscle mover of the shoulder which extends, adducts and medial rotates humerus at shoulder________?
Latissiums dorsi

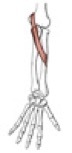
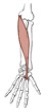
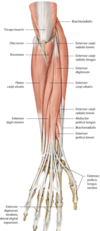
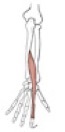
Flexor pollicis longus
Origin
Insertion

anterior surface of radius and interosseous membrane
base of the distal phalanx of the thumb

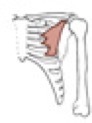
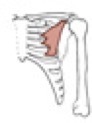
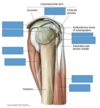
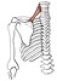
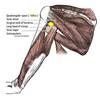
Triceps brachii
Origin
Insertion

long head: infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula; lateral head: posterolateral humerus & lateral intermuscular septum; medial head: posteromedial surface of the inferior 1/2 of the humerus
olecranon process of the ulna
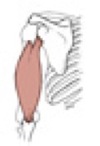
Notes on opponens digiti minimi
opposition is a rotational movement of the 5th metacarpal around the long axis of its shaft; opponens digiti minimi, abductor digiti minimi, and flexor digiti minimi brevis are in the hypothenar compartment of the hand
Notes on anconeus
(Greek, anconeus = elbow)
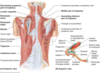
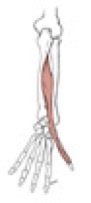
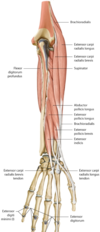
Notes on flexor digitorum superficialis
median nerve travels distally in the forearm on the deep surface of the flexor digitorum superficialis m.
Action of coracobrachialis
flexes and adducts the arm
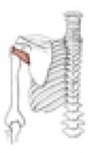
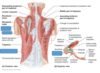
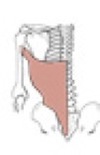
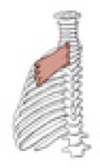
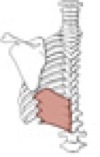
Rhomboideus major
Origin
Insertion
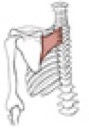
spines of vertebrae T2-T5
medial border of the scapula inferior to the spine of the scapula

Innervation of rhomboideus minor

dorsal scapular nerve (C5)

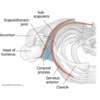
Innervation of abductor digiti minimi (hand)
deep branch of the ulnar nerve
Innervation of flexor carpi ulnaris
ulnar nerve
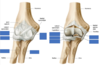
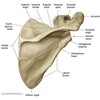
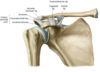
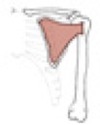
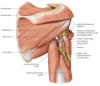
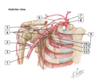
•Glenohumeral stabilizers of the shoulder
-
-
-
-( )
- Supraspinatus*
- Infraspinatus*
- Teres minor*
- (Subscapularis*)
Notes on triceps brachii
long head of the triceps separates the triangular and quadrangular spaces (teres major, teres minor and the humerus are the other boundaries); all three heads of origin insert by a common tendon
Bachial Plexus

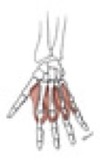
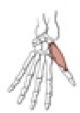
Interosseous, palmar
Origin
Insertion

four muscles, arising from the palmar surface of the shafts of metacarpals 1, 2, 4, & 5 (the 1st palmar interosseous is often fused with the adductor pollicis m.)
base of the proximal phalanx and extensor expansion of the medial side of digits 1 & 2, and lateral side of digits 4 & 5

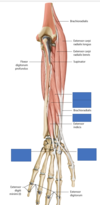
Notes on abductor pollicis longus
the tendons of abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis make the lateral border of the anatomical snuffbox (Latin, pollicis = the thumb)
Notes on latissimus dorsi
the inserting tendon twists so that fibers originating highest insert lowest (Latin, latissimus = broadest)
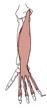
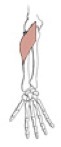
Brachioradialis
Origin
Insertion

proximal two-thirds of the lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus
lateral side of distal radius