URI, Pharyngitis, Tonsillitis (guest lecture) Flashcards
(76 cards)
Some manifestations of URIs
-nose: rhinitis, rhinosinusitis -tonsils: tonsillitis -phrynx: phryngitis -often a combination of these
What percentage of URIs is viral?
90%
What are examples of viruses that cause URIs
“cold viruses” like adenovirus & rhinovirus; -influenza: uncommon, more severe sx’s
What are some bacteria that may cause a URI
strep. pnuemo> H. flu > M. cat.
transmission of cold virus
air, hand-to-face
prevention of transmission of cold virus
wash hands; avoid close contact, mask
Treatment of URIs given percentage that are viral
90% viral, so no abx
How many days do you hold off abx with URI
hold off 7 days unless strep is suspected
When do bacteria start to accumulate and become a problem with URIs?
more than 7 days- then may give abx
Main goal with treatment for URIs
treat symptoms so patient feels better
What are sx of URIs you would treat?
- runny nose: OTC antihistatmines; ipratropium spray
- congestion - decongestants
- thick secretions- guaifenesin makes more thin and runny
Most common cause of non-infectious rhinitis & characteristics
allergies -sneezing itchy, runny nose, nasal congestions -not chronic, no sudden onset, no fever
sx with pregnancy-caused non-infectious rhinitis
pregnancy (nasal congestion with or without runny nose, no fever, no purulence)
causes of non-infectious rhinitis
allergies and pregnancy
What does Waldeyer’s Ring include?
adenoids, palatine tonsils, lingual tonsils
What are tonsils also called and what type of organ are they?
tonsils=adenoiods; they are secondary lymphatic organs
What do tonsils do?
lymphatic organs; secrete topical IgA, and IgG & IgM in to blood
What are causes of stomatitis (mouth)
usually viral - aphthous ulcers, herpangina, herpes simplex -fungal - candida/thrus
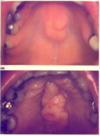
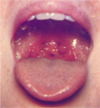
What causes herpangina?
coxsackievirus A
sx of herpangina
fever, sore throat, rash/ulcers on palate –> small vesicles with erythematous base that become ulcers -pain can be severe
What type of tx for herpangina?
supportive tx - “stomatitis cocktail”
Pharyngitis causative organism
>90% viral
What body part does pharyngitis refer to?
internal throat
symptoms of viral pharyngitis
runny nose, cough, with/without conjunctivitis, with/without diarrhea