Vertigo Flashcards
(16 cards)
Will vertigo occur in patients w amino glycoside toxicity? What is a common manifestation of bilateral vestibular loss?
Aminoglycoside - both vestibular end organs are equally affected and there is no marked vestibular asymmetry Impaired balance w/o vertigo - common manifestation of bilateral vestibular loss
Dizziness a. What should raise suspicion of superior canal dehiscence b. What does recent viral sx suggest?
a. 1. Loud noises - Tullio phenomenon 2. Coughing/ sneezing b. Vestibular neuritis
Stroke findings on HINTS test
INFART
Impulse Normal - Bilaterally normal
Fast-phase Alternating - direction-changing nystagmus
Refixation on Cover Test - looking for skew deviation
What does test of skew test for?
What is done?
Non-paralytic prenuclear vertical ocular misalignment due to brainstem/ cerebellar lesions causing imbalance of articular inputs to oculomotor sys
Detected by alt. cover test
Ddx - skew deviation and 4th n palsy
Otologic exam
a. Device used
b. What is positive vs negative
c. What is false-negative
d. Interpret Weber test
a. 512 Hz tuning fork
b.
Positive i.e. AC> BC = normal hearing/ sensorineural hearing loss
Negative i.e. BC > AC = conductive hearing loss
c. Occur if there is severe SNHL - BC stimulus Is heard in non-tested ear through transcranial transmission
d. Weber test usually lateralise away from an ear w/ SNHL or toward an ear w/ CHL
BPPV
a. Path
b. Arises from where?
c. Clinical feature
a. Dislodged otoconia from utricle that are trapped in semicircular canal
b. Posterior semicircular canal
c. Recurrent vertigo episodes lasting <1min , provoked by specific head movements e.g. look up, lying down, rolling over in bed
BPPV
Diagnosis
Dix-Hallpike manoeuvre
- With the patient sitting upright, the head is turned 45 degrees to the testing side to align post. canal w/ sagittal plane of body
- Patient Is then placed supine so that the head hangs over the edge of the bed at an angle of 20 degrees
Positive manoeuvre - provoke vertigo and a nystagmus that is up-beating and torsional w/ the top poles of eyes beating toward the lower affected ear
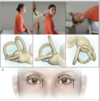
BPPV - Main Treatment
Other tx
Epley manoeuvre
- Dix-hallpike manœuvre
- Head is turned 90degrees towards unaffected side
- Head is then turned another 90 degrees to a face-down position
- Sitting position
Posterior canal occlusion - surg for v. small no. of patients
Meniere’s disease
a. Path
b. What happens during an acute attack
a. Endolymphatic hydros - overproduction/ impaired absorption of endolymph
b. Excessive end-lymphatic fluids pressure causes distension and rupture of Reissner’s membrane
Meniere’s disease
Clinical features
- Episodic vertigo - persists from 20m -12hr + N/V
- Sensorineural loss - positive Rinne and contralateral Weber
- Tinnitus
- Aural fullness - feeling of pressure in the affected ear
Meniere’s disease
Ix, most common finding
Pure tone audiometry - low frequency SNHL
Pure tone audiometry - Interpret
a. Normal
b. CHL
c. SNHL
a. AC and BC thresholds closely follow in the range of 0-20dB
b. BC is normal but AC is reduced, giving an air-bone gap
c. SNHL - both AC and BC are reduced

Meniere’s disease
a. Tx of Acute attack
b. Prophylactic treatments
a.
- Anti-histamines
- Benzodiazepines
b.
- Low-salt diet and diuretics
- Betahistine - vasodilator to reduce end-lymphatic
Meniere’s disease - Mx for intractable disease
a. W/ preserved hearing in affected ear
b. W/ complete hearing loss in affected ear
a.
- Endolymphatic sac decompression
- Vestibular neurectomy
b.
- Intratympanic gentamicin - destroy hair cells
- Labyrinthectomy - destruction of bony and membranous labyrinth
Vestibular neuritis - Mx
- Vestibular suppressants - antihistamines, BZD
- Corticosteroids
- Vestibular rehab
Superior canal dehiscence
a. Pathophysio
b. Clinical features
c. Diagnosis
a. Bone overlying the superior aspect of canal becomes thin/ even absent
b. Sound/ pressure-induced vertigo
c. High-resolution CT


