Virology Flashcards
(389 cards)
What infection in a patient with a CD4+ count <100 cells/mm3 presents with non-specific systemic symptoms and lymphadenitis?
Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare or Mycobacterium avium complex infection
What is the most salient clinical difference between opportunistic infections of Candida albicans and Epstein-Barr virus?
White plaques are scrapable in oral thrush (Candida albicans) whereas white plaques of oral hair leukoplakia are unscrapable (Epstein-Barr virus)
Of the dengue and Chikungunya viruses, which is more likely to cause severe clinical symptoms that could lead to death?
Dengue (neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhage, shock)
What molecular characteristic allows the hepatitis C virus (HCV) to evade host antibodies?
HCV lacks 3′-5′ exonuclease activity → no proofreading → antigenic variation of HCV envelope proteins and new viral mutant strains
Which 2 RNA viruses do not replicate in the cytoplasm?
Retrovirus and influenza virus (retroflu is outta cyt [sight])
What stage of hepatitis B infection does positive hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), hepatitis B e antibody (anti-HBe), and hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc IgG) indicate?
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) and low infectivity
Which 3 herpesviruses are transmitted via sexual contact?
Herpes simplex virus-2 (HSV-2), cytomegalovirus, and human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8)
In patients with HIV, what virus can cause progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)?
JC virus (polyomavirus, Junky Cerebrum)
Why can hepatitis D (HDV) infection only occur in conjunction with hepatitis B (HBV) infection?
HDV is a defective virus so it depends on the HBV HBsAg coat for entry into hepatocytes
If the intracellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1) receptor is blocked, what virus will have difficulty infecting the cells?
Rhinovirus (binds to ICAM-1); “I CAMe to see the rhino”
What cells are infected by the Epstein-Barr virus?
Infects B cells via CD21
What possible sequela can occur in mumps, especially after puberty?
Sterility
What are the symptoms associated with dengue hemorrhagic fever?
Dengue fever with bleeding and plasma leakage (thrombocytopenia) and extremes in hematocrit (high or low)
Describe how the genome of progeny virus is obtained from completed partial dsDNA.
Host RNA polymerase transcribes mRNA from viral DNA; DNA polymerase then reverse transcribes viral RNA to DNA
What do IgG antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg) signify?
Chronic infection or prior exposure to hepatitis B
What is the RNA structure of the rhabdovirus?
Enveloped, single-stranded, negative-sense, linear RNA with a helical capsid
What is the incubation period for Ebola?
Up to 21 days
What is the pathology that leads to dengue shock syndrome?
Plasma leakage leading to circulatory collapse
Compare the incubation periods of hepatitis A, B, C, and E.
Hepatitis A and E: short (weeks); B and C: long (months)
What is the purpose of neuraminidase antigen on the parainfluenza viral membrane?
Promotes progeny virion release (neuraminadaways sends virus away)
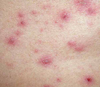
What is the pathophysiology of the “blueberry muffin” rash seen in congenital rubella?
Dermal extramedullary hematopoiesis
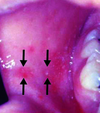
What endoscopic and biopsy findings are seen in Candida albicans esophagitis?
White plaques on endoscopy; biopsy shows yeast and pseudohyphae
Name 4 medically significant conditions caused by bunyaviruses.
Hantavirus infection (hemorrhagic fever, pneumonia), California encephalitis, Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, Sandfly/Rift Valley fevers
What predisposing factor significantly increases the risk of developing dengue hemorrhagic fever?
Infection with a different dengue virus serotype after initial infection (due to antibody-dependent enhancement of disease)