Vision L3 Flashcards
(75 cards)
is the retina a thin neural sheet?
yep
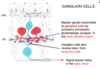
The retina is a thin neural sheet which, in addition to the photoreceptors themselves, contains four major classes of interneurons:
what are they?
bipolar cells (BC),
horizontal cells (HC),
amacrine cells (AC) and
ganglion cells (GC)
There are also glial elements known as …
(retina sheet)
There are also glial elements known as Müller cells (MC).
terina has _ well defined layers
5 layers
These cells are distributed in five well-defined layers, which can be subdivided into three ____ layers (containing cell bodies) and two _____ layers (containing axons and cell processes).
These cells are distributed in five well-defined layers, which can be subdivided into three nuclear layers (containing cell bodies) and two plexiform layers (containing axons and cell processes).


descibe the outer uclear layer
photoreceptor cell bodies
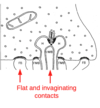
describe the Outer plexiform layer (OPL
synapses between photoreceptors, bipolars and horizontal cells.
describe the Inner nuclear layer (INL)
bipolar, horizontal and amacrine cell bodies
describe the Inner plexiform layer (IPL)
synapses between bipolar, amacrine and ganglion cells.
describe the Ganglion cell layer (GCL)
cell bodies of ganglion cells.
describe the direct pathway of information flow in the retina
which neurotransmitter do they use?
The direct pathway of information flow is from photoreceptors to bipolar cells (IB/FB) to ganglion cells (G).
All of these cells use glutamate as neurotransmitter.
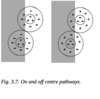
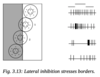
describe lateral inhibition
Lateral inhibition is mediated by horizontal cells (H) which are GABA-ergic.
Amacrine cells (A) mediate a diverse collection of interactions in the inner retina, and use many different transmitters.
Photoreceptors synapse only with _____ cells and -_____ cells;
Photoreceptors synapse only with bipolar cells and horizontal cells;
ganglion cells receive input from _____ and ______ cells.
ganglion cells receive input from bipolar and amacrine cells.
The output of the retina is carried by the axons of ganglion cells, which together form the _____ nerve.
The output of the retina is carried by the axons of ganglion cells, which together form the optic nerve.
Synaptic processing is characterised by both
____ and _____- of signals
Synaptic processing is characterised by both
convergence and divergence of signals
Ganglion cell axons are the ONLY output (together forming the optic nerve).
is there any input into the retina?
Ganglion cell axons are the ONLY output (together forming the optic nerve).
No efferent input to retina
Apart from ______ cells, all use ______ potentials
Apart from ganglion cells, all use graded potentials
which retinal cells use APs
ganglion cells
amacrine cells usually only fire spikes in response to _____ stimuli.
amacrine cells usually only fire spikes in response to strong stimuli.
why are graded potentials used in the retina?
Graded potentials are a more efficient means of
transmitting information over short distances.
Overall, the retina exhibits ________, possessing 6 million cones, 120 million rods, but only 1.5 million ganglion cells
Overall, the retina exhibits convergence, possessing 6 million cones, 120 million rods, but only 1.5 million ganglion cells
is divergence even across the retina?
the retina does not sample and process visual information uniformly.
The highest resolution is achieved only in foveal regions where there are ~3x more ganglion cells than cones (net divergence); but in peripheral retina there is only one ganglion cell for every ~16 cones (net convergence and loss of spatial information).