viva Flashcards
(30 cards)
Describe the anatomical position
The body is assumed to be
- standing,
- feet together,
- arms to the side, and
- head and eyes and palms of the hands facing forwards
Can you describe some of the planes of the body
- coronal (frontal) = vertical plane dividing body/organ into anterior and posterior parts
- sagittal = vertical plane dividing body/organ into right and left parts
- transverse = horizontal plane dividing body/organ into superior and inferior parts

Give a definition for flexion, extension, abduction, adduction
flexion = describes a bending movement that decreases the angle between two parts e.g. bending at the elbow
extension = describes straightening movement that increases the angle between body parts
abduction = movement away from the midline in a coronal plane
adduction = movement towards the midline in a coronal plane
What bony landmarks make up the thoracic cavity?
- clavicles,
- sternum,
- ribs,
- costal cartilages,
- thoracic vertebrae
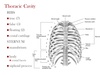
What is the function of the thoracic cage?
- Protects underlying viscera
- Muscle attachment
Identify the costal margin, thoracic Inlet (superior thoracic aperture), thoracic outlet.
•Superior thoracic aperture (Inlet) formed from
- body of T1,
- 1st Rib and
- manubrium.
•Known as outlet syndrome!
•Inferior thoracic aperture (Outlet) formed from
- body T12,
- rib 11 and 12.
- Costal cartilage of rib 7-12 and
- xiphoid process

What are the boundaries of the thoracic inlet?
Thoracic inlet boundaries:
- Posteriorly* - first thoracic vertebra T1
- Laterally* - the first pair of ribs
- Anteriorly* - the costal cartilage of the first rib and the superior border of the manubrium

What are the boundaries of the thoracic outlet?
Thoracic outlet boundaries:
- Posteriorly* - T12 vertebra ,
- Laterally* - 11th and 12th ribs,
- Anteriorly* - costal cartilages ribs 7-10, and
- Anteriorly* - xiphoid process (anteriorly – costal margin)
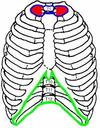
What structure separates the thorax from the abdomen?
diaphragm
Identify parts of the sternum
– divisions and important features
(e.g. jugular notch/suprasternal notch, sternal angle/angle of Lewy).
- manubrium,
- body of sternum,
- xiphoid process.

What rib articulates to the sternal angle?
rib 2

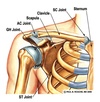
Identify parts of the scapula

- acromion and coracoid process,
- spine of scapula

What is the name of the joint connecting the sternum and clavicle?
sternoclavicular joint

What is the name of the joint connecting the acromion and clavicle?
acromioclavicular joint
Pick up a thoracic vertebrae and explain its main features
Then join two thoracic vertebrae together – locate the intervertebral foramina and explain what structures pass through here.
What structure do you find between vertebrae? Application: Slipped disc
Main features
- Articular facets – superior and inferior = for intervertebral attachments
- Costal demifacets and costal facet of transverse process = rib attachment
Intervertebral foramen – for spinal nerve
Between vertebrae
- Intervertebral disc

Name three structures that go through the thoracic inlet?
Thoracic inlet: any of
- trachea,
- oesophagus,
- thoracic duct,
- phrenic nerve,
- vagus nerve,
- common carotid arteries,
- subclavian arteries,
- internal jugular veins,
- brachiocephalic veins,
- subclavian veins….etc
Name three structures that go through the thoracic outlet?
Thoracic outlet: include the
- IVC,
- oesophagus,
- abdominal aorta,
- thoracic duct (pass through diaphragm)
Rib structure: orientate it as it would be in anatomical position.
Identify elements of a typical rib.
Articulate rib with partner vertebrae.
head of rib articulates to corresponding vertebrae e.g. rib 5 to T5
at: the superior costal demifacet of the vertebra,
and costal facet on transverse process (joins with tubercle of rib)

How many ribs are there?
Why are some ribs different to each other?
What are these called?
True
– 1-7 – attach to the sternum directly (via their own costal cartilages)
False
– 8-10 – attach to the sternum indirectly via costal cartilages of the ribs above them
Floating
– 11-12 – don’t attach to the sternum

Find the costal/subcostal groove on a rib.
What structures pass through this? In what order?
Where would you insert a chest drain – superior or inferior to the rib – why?
- diagram
-
structures -Intercostal vein, artery and nerve – VAN
i. e. the intercostal neurovascular bundle (lies between the internal and innermost muscle layers) - chest drain - Superior to rib – i.e. in lower part of intercostal space (away from neurovascular bundle)

What is the connective tissue layer that covers the muscles of the thoracic wall called?
investing fascia
Identify pectoralis major.
What are its attachments (i.e. origin and insertion – what is meant by these terms?)?
What is its function?
What is the nerve supply to this muscle?
What type of muscle is it?
Attachments
Origin
- medial half clavicle (clavicular head),
- anterior sternum and
- 1-7 costal cartilages (sternocostal head)
Insertion =
- lateral lip of intertubercular groove
Nerves = medial and lateral pectoral nerves
Arteries = pectoral branch of thoracoacromial trunk (comes from axillary artery)
Action = Adduction, flexion and medial rotation
Convergent muscle
(The origin is the fixed attachment, while the insertion moves with contraction)
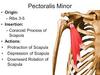
Identify pectoralis minor.
What are its attachments (i.e. origin and insertion)?
What is its function?
What is the nerve supply to this muscle?
Attachments
Origin = surface ribs 3,4,5
Insertion = coracoid process
Nerves
medial pectoral nerves
Arteries
pectoral branch of thoracoacromial trunk
Actions
moves shoulder anteriorly and inferiorly (depresses shoulder and protracts scapula)
Identify the deltoid muscle.
What are its attachments (i.e. origin and insertion)?
What is its function?
What is the nerve supply to this muscle?
Origin =
- spine of scapula,
- acromion,
- lateral third clavicle
Insertion = Deltoid tuberosity of humerus
Nerves = Axillary nerve (C5 C6)
Action = Abducts arm (after 15 degrees), flexion and extension of arm





