Weak 1: Brain Flashcards
(244 cards)
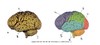
What are the 3 main parts of the brain?
- cerebrum
- cerebellum
- brainstem
What are the 3 main parts of the brainstem?
- midbrain
- medulla
- pons
What are the 2 main components of the cerebrum?
- cerebral hemisphere
- diencephalon
What are the 2 main parts of the diencephalon?
- thalamus (relay to cortex)
- hypothalamus (control of autonomics)
What are the 4 main parts of the cerebral hemisphere?
- cerebral cortex
- basal ganglia
- hippocampus
- amygdala
List the 5 lobes of the cerebral cortex?
- frontal (Motor cortex)
- parietal (Somatosensory cortex)
- occipital (Visual cortex)
- temporal (Auditory cortex)
- limbic (Drives, emotions, memory)
basal ganglia divides into what 2 parts?
- caudate nucleus
- lenticular nucleus
What is the BASIC function of the cerebellum?
coordination
What is the BASIC function of the hypothalamus?
autonomics + homeostasis
What is the BASIC function of the thalamus?
relay to cortex
What is the BASIC function of the basal ganglia?
movement control
What is the BASIC function of the frontal lobe?
motor cortex
What is the BASIC function of the parietal lobe?
somatosensory cortex
What is the BASIC function of the occipital lobe?
visual cortex
what is the BASIC function of the temporal lobe?
auditory cortex
What is the BASIC function of the limbic lobe?
drives, emotions and memory
What is the BASIC function of the hippocampus/ amygdala?
limbic structures; associated with drives, emoitions and memory
What are the 2 classes of cells in the nervous system?
- neurons
- neuroglial cells
What are the main functions of neurons?
Neurons are a functional unit of the NS that recieve and transmit neural signal in the form of action potentials.
(True or false) cerebral hemisphere includes structures deep to those on surface.
true
anterior is also known as ______
ventral
posterior is also known as ______
dorsal
the top of the brain would be known as _______
dorsal
What would the bottom of brain be known as? why?
ventral. dorsal and ventral are homologous to posterior and anterior and used synonymously in most cases, but as the brain started off as a rod like structure - the dorsal (posterior) aspect grew out to be on top. Now it is just the nomenclature