Week 1 Flashcards
(163 cards)
Define the components of the nervous system
CNS - brain, spinal cord
PNS - 12 pairs of cranial nerves, 31 pairs of spinal nerves and their branches
Enteric nervous system - found in the digestive system from oesophagus to rectum, neurones of which are found largely in one of two plexuses in the walls of the gut - myenteric plexus and the submucosal plexus
What is the most numerous cell in the CNS?
Name the 4 types that there are of this cell within the CNS
Glial cells are the most numerous cell type in the CNS
4 major types are astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia and ependymal cells
What are astrocytes and what do they do?
Type of glial cell in the CNS
Has many roles, including providing physical support and repair, maintaining the BBB and environmental homeostasis, including the removal of excess potassium ions
What are oligodendrocytes and what do they do?
What condition is are they characteristically affected in?
Type of glial cell, produce myelin in the CNS
Characteristically affected in multiple sclerosis
What are microglia and what do they do?
Type of glial cell. Specialised CNS phagocytes that have a similar lineage to macrophages. Have both immune monitoring and antigen-presenting functions.
They are haemopoietic and migrate to the CNS
What are ependymal cells and what do they do?
Type of glial cell. Ciliated cuboidal/columnar epithelial cells that line the ventricles
Again, list the different types of glial cells found in the CNS.
What types of glial cells exist in the PNS?
CNS - astrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells and oligodendrocytes
PNS - Schwann cells and satellite cells
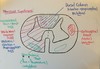
Describe the distribution of white and grey matter in a) the brain and b) the spinal cord
Brain - WHITE matter is on the INSIDE and is made up mostly of myelinated axons and their support cells. GREY matter is on the OUTSIDE and consists of a huge number of neurones, cell processes, synapses and support cells
Spinal cord - WHITE matter is on the OUTSIDE while GREY matter is on the INSIDE
Sensation arrives in the anterior/posterior horns of the grey matter of the spinal cord
Motor signals leave the anterior/posteroior horns of the grey matter of the spinal cord
Sensation arrives in the POSTERIOR (dorsal) grey matter horns
Motor signals leave the ANTERIOR (ventral) grey matter horns

The cerebral hemispheres in the adult are derived from what embryonic structure?
Telencephalon
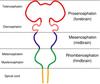
The thalamus and hypothalamus in the adult are derived from what embryonic structure?
Diencephalon

The midbrain in the adult is derived from what embryonic structure?
Mesencephalon
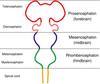
The pons and cerebellum in the adult are derived from what embryonic structure?
Metencephalon
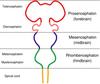
The medulla oblongata in the adult is derived from what embryonic structure?
Myelencephalon

What is the corpus callosum and what processes is it involved in?
Large white matter tract that allows communication between the left and right hemispheres
Surrounded by the cingulate gyrus
Involved in memory and motion (among other things)
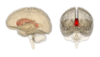
What is the lentiform nucleus? What structure is it next to and what is it made up of?
Triangle of grey matter sitting next to the thalamus and is just lateral to the internal capsule
Made up from the putamen and the globus pallidus

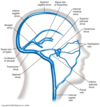
What arteries make up the Circle of Willis?
The vertebral arteries coming together to form the basilar artery
The internal carotid arteries
(The middle cerebral arteries are not actually considered part of the circle!)
The anterior cerebral arteries (+anterior communicating artery)
The posterior cerebral arteries (+posterior communicating arteries)

Which parts of the brain do the following arteries supply?
- anterior cerebral
- middle cerebral
- posterior cerebral
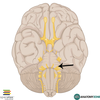
Anterior cerebral supplies mainly the superior and anterior portions of the brain (in a mohawk distribution)
Middle cerebral supplies the majority of the temporal and parietal lobes
Posterior cerebral supplies most of the occipital lobe

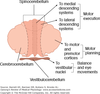
What is a collection of nerve cell bodies called when it is in a) the CNS and b) the PNS?
CNS - collection of nerve cell bodies is called a nucleus
PNS - collection of nerve cell bodies is called a ganglion
The cell bodies of multipolar neurones are found in the CNS/PNS and the cell bodies of unipolar neruones are found in the CNS/PNS
Multipolar neurone cell bodes are found in the CNS
Unipolar neurone cell bodies are found in the PNS
Motor (efferent) fibres move in what direction?
Sensory (afferent) fibres move in what direction?
Motor (efferent) - move towards the body wall/cavity or organ
Sensory (afferent) - move towards the brain
CN I - name, sensory or motor, where does it connect to?
CN I - olfactory
Sensory (special)
Connects to the forebrain
CN II - name, sensory or motor, where does it connect to?
Optic nerve
Sensory (special)
Connects to the forebrain
CN III - name, sensory or motor, where does it connect to?
Oculomotor
Motor
Connects to midbrain