White Lesions (new) Flashcards
(37 cards)
White Surface Lesions
Epithelial Thickening
Asymptomatic
Rough
DO NOT rub off
12 White Lesion Epi Thickening
- White SPonge Nevus
- Frictional Keratosis
- Hairy Tongue
- Hairy Leukoplakia
- Lichen Planus
- Leukoedema
- Geographic Tongue
- Lichenoid Reaction
- Nicotinic Stomatitis
- Smokeless Tobacco Keratosis
- Linea Alba/ Morsicatio
- Leukoplakia
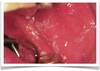
White Sponge Nevus Apperance
- Multiple white rough surface lesions through out oral cavity
- Symmetrical
- Thickened
- Corrugated/velvety
- Diffuse plaques
- Bilateral on buccal mucosa
- Also on ventral tongue, labial/alveolar mucosa, soft palate, floor of mouth
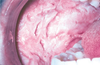
White SPonge Nevus
Cause
Tx
- Autosomal dominant inheritance
- Mutation of keratin gene, abnormal production
- May involve anal and genital
- Other family memeber may have
- Appears in early childhood
- Not premalignant
- No tx needed
Frictional Keratosis
Apperance
Cause
Treat

- White due to chronic rubbing/friction
- Anywhere in oral cavity
- Should resolve after removal of causative agent
- Otherwise no tx needed
Hairy Tongue
Apperance
Cause
Treat
- Elongation of filiform papilae due to accumulation of keratin on the dorsumof tongue
- Associated with lack of abrasion of tongue
- Treat; brush or scrape
Hairy Leukoplakia
Apperance
Cause
Treat
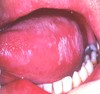
- Epithelial thickening of the lateral surfaces of the tongue
- Thickened parakeratin
- Surface corrugations
- Acanthotic epithelium
- Present in immunocompromised patients HIV, transplant
- Treat: None
Leukoedema
Apperance
Distribution
Cause
Diagnosing
Treat
- Apperance
- White, opalescent, filmy, folded surface, not rough
- Distribution
- bilateral buccal mucosa
- Cause
- common, asymptomatic, more easily recognized in African Americans
- Diagnose
- white apperance decreases when stretched
- No treatment needed
Erythema Migrans
Distribution
Apperance
Due to
Treat

- Commonly seen on ant 2/3 tongue and ventral and lateral surfaces
- Apperance
- Red patches with white border
- multiple well-demarcated, irregular, sharply defined tortous, yellow-white border
- Due to atrophy of filiform papillae with elevated white border
- Treat
- not needed, topical steroids for symptomatic lesions
Lichen Planus
Cause
Distribution
- Common dermatoligical disease
- Oversensitivity reaction of T lymphocytes
- Lesions are multifocal
- Typically bilaterally buccal mucosa
Lichen Planus: Reticular Pattern
Apperance
Treat

-
Wickhams Striae
- white lacy network with underlying erythema
- Wax and wane over weeks and months
- Asymptomatic no treatment needed
- If burning then topical corticosteroids
Lichen Planus: Errosive Pattern
Apperance
Treat

- Central area of ulceration painful
- Psudomembrane with erythema and possible Wickhams
- May present as desquamative gingivitis
- Treat
- topical corticosteroids
- Flareups require reapplicatoin or prophylatic treatment
- Severe cases- Systemic Corticoid therapy
Lichenoid Mucositis
Causes
Dist

- Clinical and micro findings similar to lichen planus
- Causes:
- Rxn to flavoring agents (cinammon mint)
- Rxn to medication
- Graft vs Host disease
- May be focal or multifocal
Nicotinic Stomatitis

- Hard palate of smokers
- No treatment
- Almost no potential for transformation to squamous cell carcinoma
Line Alba
Cause
Distribution
Treat

- Common alteration of buccal mucosa
- Pressure, frictional irritation or sucking trauma from the facial surfaces of the teeth
- Usually bilateral
- No treatment
Morsicatio Buccarum
Cause
Distribution
Apperance
Treat

- Chronic check chewing
- Labial mucosa= Morsicatio labiorum
- Tongue= Morsicatio linguarum
- Usually bilateral
- Thickened, shredded, areas of white hyperkeratosis
- No treat needed
Leukoplakia Definition
- White patch or plaque that cannot be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease
- Strictly a clinical term and does not imply diagnosis
- Dependent on the exclusion of other white lesions
Lesions that must be excluded before the term Leukoplakia can be used 9
- White sponge nevus
- Frictional Keratosis
- Hairy tongue or lukoplakia
- Leukoedema
- Geo tongue
- Lichen Planus/Lichenoid Mucositis
- Tobacco pouch hyperkeratosis
- Nicotine stomatits
- Morsicatio (chronic chewing on tissue)
Leukoplakia must be microscopically diagnosed by biopsy and will be one of the following
- Hyperkeratosis
- Epithelial dysplasia
- Epithelial dysplasia
- Carcinoma-in-situ
- Superficial squamous cell carcinoma
Hyperkeratosis
- Callous
- Not premalignant
- Does not need removal
Epithelial Dysplasia
- Atypical cells confined to the cells of the epithelium
- Considered premalignant
- mild dysplasi not removed
- Moderate may be removed
- Severe must be removed
Carcinoma In-situ
- cancer confined to the epithelium
- Will eventually invade
- MUST be removed
Superficial Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Treat
MUST be removed
White Surface Debris Lesions
- Symptomatic
- Rub off
- Underlying erythema
- Include
- Candidosis
- Burn
- Dentrifice-associated slough