1. Congenital Disorders of MSK Flashcards
(31 cards)
osteogenesis imperfecta
inherited disorder of type I collagen that results in fragile, low density bones
is OI dominant or recessive
dominant
osteogenesis imperfecta: majority of cases
multiple fragility fractures of childhood, short state with multiple deformitites, blue sclerae and loss of hearing

osteogenesis imperfecta: what can multiple fractures be mistaken for
child abuse/non-accidental injury
osteogenesis imperfecta: what can osteopenia result in
low energy fractures
osteogenesis imperfecta: what are the bones like
thin cortices and osteopenic
osteogenesis imperfecta: how may a mild case present
normal x ray with history of low energy fractures
osteogenesis imperfecta: how do fractures tend to heal and how are they treated
tend to heal with abundant but poor quality calus
treated with splintage, traction or sugical stabilisation
osteogenesis imperfecta: when Sofield procedure indicated
progressive deformities develop that require multiple osteotomies and intramedullary stabilisation for correction - sofield procedure

osteogenesis imperfecta: what is the mildest and most common form
type I
normal life expectancy

osteogenesis imperfecta: severe form
type III
recessive

skeletal dysplasias
medical term for short stature
due to geneteic error resulting in the abnormal development of bone and connective tissue
may be proportionate or disproportionate
skeletal dysplasias: what does dis/proportionate refer to
relative length of limbs and spine
achondroplasia
most common type of disproportionate short stature
short limbs with prominent forehead and widened nose
lax joints
normal mental developement
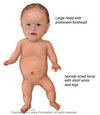
skeletal dysplasias: what testing and treatment should be considered
genetic testing of child and family
orthopedic treatment - deformity correction and limb lengthening
growth hormonal therapy may be appropriate
connective tissue disorders
genetic disorders of collagen synthesis (mainly type I) resulting in joint hypermobility
tend to affect soft tissue rather than bone (osteogenesis imperfecta)
generalised joint laxity
hypermobility present in normal population - ‘double-jointed’
people are more prone to OA, soft tissue injuries and recurrent dislocations
inheritance pattern for generalised joint laxity
dominant
how is marfans syndrome acquired
AuD or sporadic mutation fibrillin gene resulting in tall stature with disproportionately long limbs and ligamentous laxity
what may cause premature death in marfans syndrome
cardiac abnormalities
features of marfans syndrome

ehlers danlos syndrome
heterogenous condition with abnormal elastin and collagen formation
ehlers danlos syndrome: inheritance pattern
dominant
ehlers danlos syndrome: clinical features
- profound joint hypermobility
- skin is fragile, poor healing (wound dehiscence common) and easily bruised
- some forms are associated with scoliosis




