1 DNA to Protein: Transcription to Translation Flashcards
(37 cards)
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
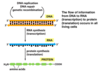
How do the phosphodiester linkages in RNA and DNA compare?
- It’s the same!
How does RNA compare to DNA?
*
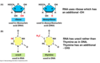
RNA 3D structure
How is it maintained?
What does it allow RNA to do?
- RNA can fold into specific 3D structures.
- 3D structures are maintained by conventional base pairing or modified by nonconventional base pairing.
- 3D structure allows RNA to catalyze its own splicing.
- RNA needs correct 3D structure to maintian enymatic function.

During Transcription the RNA strand is complementary to the _____ strand but has U instead of T.
- During Transcription the RNA strand is complementary to the template strand but has U instead of T.
How do RNA polyermases have the energy for Transcription?
- The incoming nucleosides (ATP, UTP, CTP, GTP) supply energy needed for catalysis from their triphosphate bonds.
What is the function of mRNAs?
- Messenger RNAs, code for proteins
What is the function of rRNAs?
- Ribosomal RNAs, form the basic structure of the ribosome and catalyze protein synthesis
What is the function of tRNAs?
- Transfer RNAs, central to protein synthesis as adaptors between mRNA and amino acids
What is the function of snRNAs?
- Small nuclear RNAs, function ina variety of nuclear processes, including the splicing of pre-RNA.
What is the function of snoRNAs?
- Small nucleolar RNAs, help to process and chemically modify rRNAs & Spliceosomal RNAs / mRNAs
How does RNA Polymerase know where to start/stop?
- Signals encoded in DNA tell RNA polymerase where to start/stop.
How is direction of transcription determined?
- The promoter can be on either strand but always goes 3’ → 5’
What is the TATA box and what is it’s function?
- 25 nucleotides upstream from the initiation site
- Most important DNA sequence that signals the start of Transcription.
What does RNA polymerase I transcribe?
- rRNA genes
What does RNA polymerase III transcribe?
- tRNA genes
- rRNA genes
- some snRNA genes
What does RNA polymerase II transcribe?
- All protein-coding genes (mRNA)
- snoRNA
- miRNA
- siRNA
- most snRNA
- lncRNA
What does the initation of transcription require?
- The initation of transcription requires multiple activator proteins along with proteins that unwind the chromatin.
What role do activator proteins play in transcription?
- activator proteins help coordinate the acquisition of the different proteins needed for transcription initialization.
- They also play a role in modifying DNA shape → affects rate of transcription
- *activator proteins can be located 1000s of nucleotides upstream.
Supercoiling negative/positive & Topoisomerase
- Negative supercoiling (behind RNA polymerase)
- helix opening facilitated
- Postivite supercoiling (in front of RNA polymerase)
- helix opening hindered
- Specialized proteins (topoisomerase) remove superhelical tension.
What is the first modification of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNAs?
- As soon as the mRNA is ~25 nucleotides long it is capped
- RNA Capping
How does RNA Capping work?
- 3 enzymes work together
- Dephosphorylate the 1st nucleotide
- Adda GMP in reverse linkage (5’ to 5’ instead of 5’ to 3’), and
- Add a methyl group to the guanosine
- Sometimes another methyl group is added to the ribose of the 1st nucleotide
- The cap allows mRNA to be distinguished from noncoding RNAs and is also important for establishing translation.

What is Factor VIII and how does RNA Splicing affect it?
- Factor VIII catalyzes one of the steps in the clotting cascade
- When it is mutated or deleted (incorrect splicing), the result is hemophilia.
Whats the idea of alternative splicing?
- Primary transcript can be spliced in different ways to produce distinct mRNAs which then give rise to variant proteins.
- Most alternatively spliced proteins (most protein coding genes) contain constituitive elements that are there almost all the time.








