1 Introduction to Cardiovascular System Flashcards
(47 cards)
Is the left ventricle of the heart filled with deoxygenated or oxygenated blood?
Oxygenated
Name and identify the 6 layers of the pericardium:

1-
2-
3-
4-
5-
6-
1- Fibrous pericardium
2- Parietal layer
3- Visceral layer (Epicardium)
4- Pericardial cavity
5- Myocardium
6- Endocardium

Identify the coronary arteries in red:

(LAD a.k.a Anterior interventricular artery)

Identify the major cardiac veins in the following diagram:


Identify the following arteries:


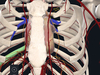
Name and identify the arteries in red shown on the upper limb:


Name and identify the veins in blue shown on the upper limb:


Name and identify the arteries in red shown on the lower limb:


Name and identify the veins in blue shown on the lower limb:


What is the role of perforating veins?
Drain blood from superficial veins to deep veins.

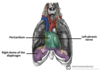
Where is the heart located?
- Middle mediastinum (area in thoracic cavity between right and left pleural sacs)
- Lies within the pericardium
- Phrenic nerve on side of pericardium

What does the pericardium consist of?
- Strong outer fibrous layer
- Inner serous membrane made of two layers

What is the oblique sinus?
Space under the heart that is a blind end, swabs can get lost in there during surgery, posterior to left atrium

What is the transverse sinus?
Allows surgeon to cut off heart by isolating aorta and pulmonary trunk

Label this diagram of the heart


Label this posterior view of the heart


Name the valves of the heart and their structure
- Pulmonary and Aortic Valve
- Mitral valve (left)
- Tricuspid valve (right)
Only bicuspid valve is the mitral valve



Label these coronary veins


Where are the renal and testicular veins?


Label all of the arteries with a dot next to them


What are the borders of the heart?

Why might the heart shadow become enlarged?
- Ventricular hypertrophy
- Pericardial effusion
- Dilated left ventricle

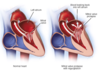
What are the sequence of changes that occur in the arterial wall to cause an arterial occlusion?
- Atheroma plaque
- Plaque ruptures
- Thrombus forms
- Embolism
(stroke in cerebral artery, MI in coronary artery)