13.2 Current diagnosis & management of CAP (Community Acquired Pneumonia) in UK Flashcards
(36 cards)
What are common respiratory tract infections?
- Acute bronchitis
- Bronchiolitis
- Pneumonia
What is the definition of pneumonia?
-
Inflammation of lung parenchyma leading to consolidation (Infection of the air-space of the lung)
- Doesn’t have to be infectious or bacterial (e.g. viruses, fungi)
- CXR changes (consolidation)
- Treated as bacterial infection
What is the definition of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP)?
- Pneumonia acquired outside hospital or healthcare facilities
What is the definition of hospital acquired pneumonia (HAP)?
- Pneumonia acquired ≥ 48 hrs. into hospital admission that wasn’t incubating on admission
Who is at risk of getting pneumonia?
- OLD (co-morbidities - COPD, HIV, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, sickle cell disease, frailty, immunosenescence - gradual deterioration of the immune system)
-
DISADVANTAGED
- Socioeconomic deprivation
-
PHARMCEUTICALS
- PPI
- Inhaled corticosteroids
- Antipsychotics
- Opioids
- Alcohol abuse
- Poor oral hygiene
-
Contact with children
*
What are the types of bacterial pathogens that cause pneumonia?
-
TYPICAL
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Haemophilius influenza
-
ATYPICAL - DO NOT respond to B-LACTAM PENICILLINS
-
Add clarithromycin in treatment regardless of CURB-65 score
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Chlamydophilia pneumoniae
-
Add clarithromycin in treatment regardless of CURB-65 score
-
OTHERS
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Enterobacteriaceae
Give examples of viral pathogens causing pneumonia
- Influenza A
- Influenza B
- Rhinovirus
- Corona virus
- COVID-19
- SARS
- Metapneumovirus
Explain the pathophysiology of pneumonia
- Inhaled
- Aspiration from oropharynx
- Direct spread
- Haematogenous spread (in blood)
From one’s history how could you detect pneumonia?
- Detecting symptoms consistent with CAP
- Chills (Fever)
- Breathlessness (Dyspnoea)
- Cyanosis
- Cough
- Sputum production
- Pleuratic chest pain
- Haemoptysis
- Arthralgia (pain in joints)
- Myalgia (pain in muscles/group of muscles)
-
Dullness to percussion
- Crackles when breathing
-
Defects of immunity
- Elderly
- Immunocompromiseed
- Risk of exosure to specific pathogens
-
LEGIONELLA
- Confusion, GI upset, lymphopaenia (decreased lymphocytes in blood), hyponatraemia (low sodium in blood)
-
MYCOPLASMA
- Young, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), myocarditis
-
LEGIONELLA
What is the differential diagnosis of pneumonia?
- Left ventricular failure
- Pulmonary embolus
- Infective exacerbation COPD
- TB
- Acute asthma
- Oesophageal rupture
At what point could you consider that the pneumonia is due to ‘atypical pathogens’?
- Foreign travel (all atypicals)
- Prior antibiotics, hyponatraemia (mycoplasma)
- Air conditioning exposure
- Diarrhoea
- Abnormal LFT’s
- Neurological symptoms
- Headache (Chlamydophila pneumoniae)
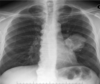
What is the purpose and findings on a CXR for pneumonia?
- To confirm diagnosis of ‘suspected CAP/HAP’
- Consolidation will be seen
- If little clinical signs but severe = legionella/myoplasma
- Needs to be done within 4 hours of admission and CAP confirmed within this time
What is a CURB-65?
- Confusion (AMTS (abbreviated mental test score) <=8/10)
- Urea (>7mmol/L)
- RR (>= 30breaths/min)
- BP (SBP <90mmHg, DBP <= 60mmHg)
- Age >65 years old
1 point awarded for each category if in zone (thus, out of 5 points)
No bloods needeed for CRB-65
Needs to be recorded in NOTES
What to determine from CURB-65?
- Based on scoring = severity:
- LOW = 0-1 = <3% mortality risk
- MODERATE = 2 = 9% mortality risk
- HIGH = 3-5 = 15-40% mortality risk
- The HIGHER risk of death = treat MORE aggressively (& decides what kind of treatment needed)
What is the ATS/IDSA criteria for severee CAP?
To have SEVERE CAP must be 1 major category or 3+ minor categories
-
Major criteria
- Respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation
- Septic shock with the need for vasopressors
-
Minor criteria
- Respiratory rate ≥30/minute
- Confusion/disorientation
- Urea ≥7.14 mmol/L
- Leukopenia due to infection alone WBC < 4 x 109
- Thrombocytopaenia < 100
- Hypothermia, temp < 36
What is PSI (pneumonia severity index)?
- Is a tool used to put patients into risk classes (1-5):
- DEMOGRAPHICS (study of a population based on factors such as age, race, and sex)
- CO-MORBIDITIES
- PHYSICAL EXAM/VITAL SIGNS
- LABORATORY/IMAGING
- When risk class 4-5 recommended site of care = INPATIENT (other classes = outpatient care)
What are routine bloods for someone with pneumonia?
- FBC
- U&E’s
- LFT’s
- CRP
- Procalcitonin
- ABG’s (SpO2 <94%)
What tests to do if someone has medium - high severity CAP (CURB-65 >=2)?
- Sputum test
- Pneumococcal/legionella urinary antigen testing
- Paired serology (scientific study of serum and other body fluids) if not responding to treatment
What tests would you do if someone is young and has pneumonia (mild)?
- HIV testing
- Test for TB (as may need isolating) (AFB - acid fast bacillus = shows active TB)
Consider the different management options with severity of pneumonia
-
LOW severity = Consider home treatment (CURB-65 = 0-1) –> if no unstable co-morbidities
- 1st line: Amoxicillin
- Alternatives: Clarithromycin or Doxycycline
-
MODERATE severity = (CURB-65>=2) –> hospital treatment also if lower score but unstable co-morbidities
- 1st line: Amoxicillin
- Alternatives: Clarithromycin
-
SEVERE = (CURB-65 >= 3) –> consider CCU (critical care unit) treatment and transfer
- 1st line: Co-amoxiclav
- Alternative: Cefuroxime
ALL patients oxygen given to keep SpO2 94-98% (or if COPD 88-92%)
What are the contraindications to outpatient therapy?
- Inability to maintain oral intake
- History of substance abuse
- Severe comorbid illnesses
- Cognitive impairment
- Impaired functional status
- Availability of support at home
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a lung ultrasound in pneumonia?
-
ADVANTAGES
- Quick
- Simple
- Cheap
- Reliable
- Assess pleural collections
-
DISADVANTAGES
- Miss diagnosis (interstitial pneumonias)
- Diffuse disease

Explain the use of a chest CT in diagnosis of pneumonia
- Most information
- Access, ionizing radiation
- 5% admission CXR non-diagnostic,
- CT confirmation

Step by step when patient comes in with suspected pneumonia
- Perform CXR within 4hrs of admission
- Assess Oxygen Saturation and prescrube oxygen according to appropriate target range
- Calculate CURB 65 in all patients where CXR demonstrates pneumonia
- Adminster antibiotics within 4hrs of diagnosis appropriate to CURB 65 score