140 Antiarrhythmic Drug Therapy Flashcards
(47 cards)
Mechanisms/Classifications of Bradyarrhythmias
- Diminished automaticity
- Block

Mechanisms of Tachyarrhythmias
- Enhanced automaticity
- Increased phase 4 depol
- Make threshold more negative
- Renentry
- Triggered activity
- Early after depols
- •During Phase 2, 3 of AP
- Early after depols
- Ca2+ current Dependent
- Occurs in setting of prolonged APD (prolonged QT interval)
- Delayed afterdepols
- During Phase 4 of AP
- Delayed afterdepols
Associated with high Ca2+ (eg digoxin toxicity)

Supraventricular tachyarrhythmias list
oSinus Tachycardia
oAtrial Premature Beats
oParoxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
(aka Supraventricular Tachycardia aka SVT)
oAtrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)
oAtrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia (AVRT)
oEctopic Atrial Tachycardia
oAtrial Flutter
oAtrial Fibrillation
oMultifocal Atrial Tachycardia

Ventricular tachyarrhythmias list

AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)

Atrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia (AVRT)

Atrial Flutter

Atrial Fibrillation

Ventricular Tachycardia

Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia

Ventricular Fibrillation

Treating Enhanced Automaticity (theory)
- •Make maximum diastolic potential more negative
- •Reduce slope of phase 4 depolarization
- •Make the threshold potential more positive
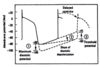
Treating Reentry (theory)
Disrupt the Balance
- e.g. slow the “slow conduction” even more so it blocks
- supress premature beats which often set up slow conduction

Treating Triggered Activity (theory)

Rate Control vs. Rhythm Control in Atrial Fibrillation

Vaughan-Williams Classification

Na+-Channel Blockers Mechanism

Na+-Channel Blockers: Effect on Phase 0
Na+-Channel Blockers: Effect on Action Potential Duration

Procainamide
Class 1A
•Drug-induced Lupus: arthralgia, pleuritis, pericarditis with PO (not clinically available)
•Torsades de Pointes:
N-acetylprocainamide a first pass
metabolite with strong K+ channel
activity
Quinidine
Class 1A
•Additional vagolytic effects
–eg urinary retention, constipation, blurred vision, dry mouth
•Cinchonism: CNS toxicity – tinnitus, psychosis
•Torsades de Pointes: K+ blocking activity
Disopyramide
Class 1A
- Additional stronger vagolytic effects
- Additional negative inotropic effects
•Antimuscarinic: urinary retention, constipation, blurred vision, dry mouth
•Torsades de Pointes: K+ blocking activity
Lidocaine
Class 1B

•CNS Toxicity:
confusion, delerium, grand mal seizures
good for post MI
Mexelitine
Class 1B
•CNS Toxicity:
confusion, delerium, grand mal seizures
Flecainide
Class 1C
- Potent negative inotropic effects
- Propafenone: beta-blocking effects
- Slows conduction (because of potent Na+ blocking)
•Contraindicated in LV systolic dysfunction and heart block












