14.1 The Neurobiology of Vision Flashcards
(43 cards)
Label the diagram


Label the diagram and the lobes

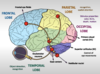
Where do the nerves from the retina go?
- The nerves leave the eye in the optic nerve and synapse in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
- Fibres then go to the visual cortex
Transmits all light information into electical information to the brain
Label the diagram

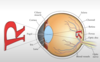
What is the purpose of the cornea?
- Involved in focusing light into eye
- Transparent covering over eye: is a barrier between outside world and inner eye
- Refracts light entering the eye
- NO blood vessels
- VERY sensitive to light
What is the purpose of the pupil?
- Small opening in eye by which light passes
- Size of pupil can change which can be due to light or emotion (e.g. like someone pupil dilates)
-
LOW light –> pupils dilate, more light into eye
- better to see when dark
-
HIGH light –>pupils constrict
- LESS light into eye
What is the iris?
- The coloured portion of the eye
- Regulates the amount of light into the eye
What is the purpose of the lens?
- Serves by focusing light to back of eye (refracts)
- Transparent structure that helps refract light onto retina
What is the fovea?
- Indentation (small) at the back of the eye where there is high level detail processing of light
- Region where upper retinal layers are THINNED
What flips the inverted image from the retina?
The vision cortex
What is vision?
Transduction of light
What produces tears?
Lacrimal gland produces tears and passes through the lacrimal ducts
What does vision depend on?
Depends on light sensitive cells in the retina at the rear of the eye
How does light reach the retina?
Light is focussed by the cornea and lens onto the retina
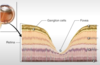
Explain the structure of the retina (layers)
& label the diagram
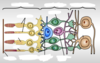
-
Photoreceptors (allow night vision)
- Made of cones and rods
-
CONES
- More in centre of retina
- Only type in fovea of eye
-
RODS
- More in outer areas of the eye
- Used for peripheral vision
- Outer plexiform layer
-
Horizontal layer
- Form synapses with bipolar cells & photoreceptor cells
-
Bipolar cell
- Connect photoreceptors to ganglion cells
-
Amacrine cell
- Translate information
- Inner plexiform layer
-
Ganglion cell
- Gets info from retina & sends onto brain (via optic nerve)
- Their axons leave the eye

What do photoreceptors do & how?
- Photoreceptors capture light
- Have outer segments with stacks of membrane that increases their surface area greatly
- Pigment molecules collect light
What is a photon?
A single unit of light
What is the wavelength of visual light and colours on the sides of the spectrum?
(BLUE) 380-750nm (RED)
Infra red Ultra-violet
What are the kinds of photoreceptors?
- 120 million RODS (more rods in nocturnal animals)
- 6 million CONES
-
RODS
- More sensitive to light and occur in the periphery (at low light)
-
CONES
- Respond to different wavelengths
- Mainly found in the fovea (day-light, when HIGH levels of light)
What are these and label them and what is the difference between the two?

The outer segments are different

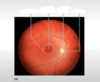
Label this fundoscopy image

Label this diagram & briefly explain it

- At the fovea (where information from the lens is focussed) there is a 1:1 ratio of photoreceptors : ganglion cells
- At the retina there is a 50:1 ratio of photoreceptors : ganglion cells
Explain receptor potentials in photoreceptors, bipolar cells, ganglion cells
-
Photoreceptors
- HYPERPOLARISING membrane potential following stimulus
-
Bipolar cells
- DEPOLARISING membrane potential
-
Ganglion cells
- Recording of action potentials then sends it to the brain
How many types of rods & cones are there?
-
Cones
- Blue
- Green
- Red
-
Rods
- Blue/green






