Midterm Flashcards
Syllabus Information
AERO 310 - Technological innovations that have led to modern aircraft and spacecraft as viewed from a historical perspective.
Ancient Myth - Kind Menos
Island of Crete, owned Menator. Daedalus and Icarus built labarynth for beast, other captors would be led, died. String to get out. Daedalus made wings made of feathers and wax, Icarus flew too close to sun, dies
Ancient symbols of aviation (7)
Cupid, Apollo, Nike (Victory Goddess), Pegasus, Mercury, angels, Elijah (flaming chariot to heaven)
Developments for Powered Flight (11)
engine/fuel, propulsion, aerodynamics (lifting surfaces, airfoils, wings), landing gear, materials, structure, configuration, controls (last), pilot skills (last), aeronautical knowledge, creativity
Aristotle & Meduim Theory
If you apply energy to an object, as long as you have that energy there, the object will continue its motion. Consistent the whole time. Ex: feather on wind
Leonardo da Vinci
(1452-1519) Human flight. Over 500 sketches, writings about it. Works were only discovered recently. Concept of Consensabilit - relative velocity was key, imagine flapping and soaring flight.
da Vinci inventions/ studies (6)
wing construction, retractable landing gear, parachute, helicopter, streamlining, gliders
da Vinci mistakes
Man could not operate anything he made because it was too heavy. Now we have human powered machines, 69 lbs. flew form Crete to Santorini in 1987.
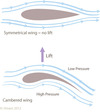
Johan and Daniel Bernoulli
(1660s-1780s) Bernoulli Principle - velocity and pressure. Send something though a tube, and have the middle skinnier, it will go much faster through the skinny middle. Low pressure in the middle and high on either side. 75% of lift

Montogolfier Brothers
(1780s) Etienne and Joseph were French paper-makers near Lyons. First aerial balloon flight, using hot air and hydrogen
Balloons in France
(mid 1800s) people began hot air-ballooning. Huge fad, but slowed down around 1875 because of French Revolution. Andre Jaques Gernerin
Andre Jacques Gernerin
French, first human to parachure form balloon at 3,000 ft.
Count Von Zeppelin

(mid 1800s) German, served in German army as general, began designing aircrafts which would later turn into blimps. Founded Zeppelin Airship Company (built Hidenburg). Interst sparked when visiting US balloon camp.
Sir George Cayley
English aristocrat, wealthy, educated. Balloons and gliders. Many developments methods
Sir George Cayley inventions
tail for stability, landing gear, bi-planes, developed cambered shape for wings and propellers. Identified forces of lift, drag and thrust, published everything
Octave Chanute
(1832-1910) Third Wright brother. Engineer. Bridge knowledge applied to wings on bi-planes. “Pratt Truss Bracing”. First great historian of aviation
Who was the first great historian of aviation, and third Wright brother?
Ocatave Chanute
Samuel Pierpont Langley
(1834-1906) American mathmatician and astronomer. Builds table-sized models that ran on steam or petrol. would stay up until ran out of fuel. Failed Aerodrome


