2/21 Breast Path - Corbett Flashcards
(35 cards)
graphic: breast anatomy
breast is modified sweat gland
organized into lobules connected to ducts connected to areola
fx unit: TDLU : terminal duct lobule unit
- two epithelial layers
- luminal (simple columnar)
- myoepithelium

diff areas of breast that can be diseased
-
nipple/areola
- intraductal papilloma
- abscess/mastitis
- Paget’s disease
-
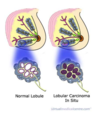
terminal duct lobular unit
- fibrocystic changes
- ductal/lobular CIS
- ductal cancer
- lubular cancer
-
stroma
- fibroadenoma
- Phylloides tumor

presentation of breast disease
- mass
- asymptomatic w pos screening test
- nipple discharge
- skin changes
[pain] - common problem, but rarely cancer
devpt of breast
mammary ridge forms at 4-5wk gestation from budding ectoderm → surrounding mesenchyme
extra thoracic milk streak typically regresses
-
if it doesnt? accessory nipple (polythelia) and mammary tissue (polymastia)
- polythelia : most common on thorax below healthy breasts
- polymastia : most often in axilla

breast infections
most commonly affects women 18-50y
usually a primary event affecting the skin overlying the breast
two types:
-
lactational (most common)
- bacterial invasion through irritated/fissured nipple → cellulitis
- second postpartum week
- assoc: milk stasis, duct obstruction
- Staph aureus most common
-
nonlactational
- ddx is critical - need to distinguish from cancer
sx: erythema, tenderness, induration, warmth, drainage, systemic sx
periductal mastitis
SMOKERS
infl condition of subareolar ducts
presents with periareolar infl
duct ectasia
can present as periareolar mass
ddx: cancer
fat necrosis of breast
50% assoc with trauma to breast
palpable mass present
proliferative changes and risk of breast cancer
can be associated with DUCTS, LOBULES, or STROMA
- non prolif breast changes (ex. fibrocystic change) → no risk
- proliferative breast disease → slight risk, 1.5-2x
- atypical hyperplasia → high risk, 4-5x

nonproliferative changes
(fibrocystic changes)
most common BENIGN breast condition
conseq of cyclical breast changes occuring with menstrual cycles
confer little/no risk of cancer
- simple cysts
- fibrosis
- adenosis (incr acini per lobule)
breast cysts
cyst rupture
30-50 age group
originate from lobule dilatation and coalescence (green, brown, clear fluid)
- if rupture**?*
- release of secretory material into adj stroma → chronic infl/fibrosis → palpable firmness of breast
histo
- flattened epithelium
- columnar epithelium with features of apocrine cells (like sweat glands)

apocrine metaplasia
cells resemble apocrine sweat glands
enlarged cells w abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, apical snouts
put lots of secretion into lumen
not a concern

adenosis
incr in number of acini per lobule
normal with pregnancy
focal finding in non-lactating breast
see: normal number of cell layers

gynecomastia
vs pseudogynecomastia
benign enlargement of glandular breast tissue in men
related to imbalance in estrogen/testosterone
- birth (high maternal estrogen)
- adolescence (hormone levels fluctuating)
- middl-aged and older men (if overweight, estrogen higher; test levels dropping)
usually bilat
see dilated ducts, periductal fibrosis
pseudogynecomastia: deposition of adipose tissue (not breast tissue)
proliferative changes
typically, incr number of cells
vary in size/shape BUT look BENIGN/normal
sclerosis adenosis
proliferative change
presents as mass or density
- incr acini
- stromal proliferation and fibrosis
masses of small glands within a fibrous stroma

intraductal papilloma
proliferative change
hyperplastic epithelial growth with a STALK (multiple papillae in complex arborizing pattern)
presents with unilateral bloody nipple discharge
usually solitary and located beneath the areola
- lactiferous sinuses
- occasionally multiple

atypical hyperplasia
INCREASED CANCER RISK : 3.7-5.3x
ducts or lobules are partially filled with relatively monomorphic proliferation of reg spaced cells (sometimes w cribriform spaces)

fibroadenomas
proliferation sof epithelium and stroma
most common benign neoplasm of breast (caused by prolif of lobular stroma)
- seen in young women 15-25
- round, well circumscribed, mobile
- often solitary
- can vary in size with menses, incr during preg → estrogen responsive

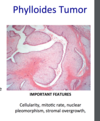
Phylloides tumor
common in 40-50y
most offten BENIGN
- assoc with chromosomal changes
key features
- cellularity
- mitotic rate
- nuclear pleomorphism
- stromal overgrowth
breast cancer
risk factors
1. AGE
2. estrogen related (breast tissue has E receptors → constant exposure if it’s overabundant)
- early menarche
- late menopause
- nulliparity
- first full term preg after 30
- obesity/incr BMI
- long term/hi dose estrogen replacement tx
3. genetic
- first degree relative with breast cancer
- genetic predisposition: BRCA1, BRCA2
- hx of breast, ovarian, endometrial cancer
4. radiation
- prior radiation to breast area (ex. tx for Hodgkin’s disease)
- high breast tissue density
genetic risks of breast cancer
1 cause: “single gene” familial BC
80-90% BRCA1 and BRCA2
- gen pop frequency: 1/400
- having confers 10-30x higher risk than genpop
- 3% of all breast cancer
BRCA genes
tumor suppresor genes
code for large, multifx proteins:
- repair of ds DNA breaks
- transcription
- ubiquitination
BRCA1 related breast cancer
early onset (under50)
high rate of bilateral breast tumors
usually high grade, aneuploid
triple negative → poor prognosis