2. Anatomy and Physiology 2 Flashcards
(174 cards)
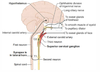
Neuromuscular junction This is the 2nd synapse in which spinal tract?
Lateral corticospinal tract
Lower vs. Upper motor neuron lesion
Lower MN lesion = everything lowered (less muscle mass, decr muscle tone, decr reflexes, downgoing toes) Upper MN = everythinig up (tone, DTRs, toes)
Spinal tract: UMN vs. LMN lesion: Weakness
Both
What motor neuron sign is present in both UMN and LMN lesions?
Weakness
Spinal tract: UMN vs. LMN lesion: Atrophy
Atrophy in LMN only
Spinal tract: UMN vs. LMN lesion: Fasciculations (muscle twitching)
Present in LMN lesions only
What motor neuron signs are only present in LMN lesions?
Atrophy and fasciculations/fibrillations
Spinal tract: UMN vs. LMN lesion: Reflexes
Increased in UMN Decreased in LMN
Does UMN/LMN lesions lead to increased, decreased or the same reflex?
UMN vs. LMN lesion: Reflexes
Spinal tract: UMN vs. LMN lesion: Tone
Increased in UMN, decreased in LMN
What is increased in UMN lesion but decreased in LMN?
UMN vs. LMN lesion: Tone
Spinal tract: UMN vs. LMN lesion: Babinski sign (upgoing toes – normal in infants)
(+) in UMN, (-) in LMN
What does Babinski sign suggest about lesion?
UMN
Spinal tract: UMN vs. LMN lesion: Spastic paralysis
(+) in UMN (-) in LMN
What lesion does clasp knife spasticity suggest?
UMN
Spinal cord lesions: Poliomyelitis and Werdnig-Hoffmann disease What areas are affected? What are the Sx?
Lower motor neuron lesion only, due to destruction of anterior horns; flaccid paralysis
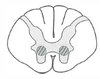
Lower motor neuron lesion only, due to destruction of anterior horns; flaccid paralysis What diseases (2) are associated with this?
Poliomyelitis and Werdnig-Hoffmann disease
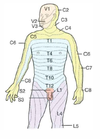
Spinal cord lesions: Multiple sclerosis What areas are affected? What are the Sx?
Mostly white matter of cervical region; random and asymmetric lesions, due to demyelination; scanning speech, intention tremor, nystagmus
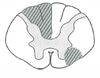
Mostly white matter of cervical region; random and asymmetric lesions, due to demyelination; scanning speech, intention tremor, nystagmus What disease is associated with this?
Multiple sclerosis
Spinal cord lesions: ALS What areas are affected? What are the Sx?
Combined upper and lower motor neuron deficits with no sensory deficit; both upper and lower motor neuron signs.
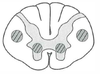
Combined upper and lower motor neuron deficits with no sensory deficit; both upper and lower motor neuron signs. What disease is associated with this?
ALS
Spinal cord lesions: Complete occlusion of the anterior spinal artery What areas are affected? What are the Sx?
Spares dorsal columns and tract of Lissauer; upper throacic ASA territory is a watershed area, as artery of Adamkiewicz supplies ASA below ~T8
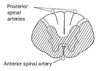
Spares dorsal columns and tract of Lissauer; upper throacic ASA territory is a watershed area, as artery of Adamkiewicz supplies ASA below ~T8 What disease is associated with this?
Complete occlusion of the anterior spinal artery
Spinal cord lesions: Tabes dorsalis (tertiary syphilis) What areas are affected? What are the Sx?
Degeneration of dorsal roots and dorsal columns; impaired proprioception, locomotor ataxia