22 - Health Improvement Flashcards
(34 cards)
What are the three domains of public health?
- Health Improvement
- Health protection
- Healthcare public health

What is the ‘left shift’ in population health?
Population strategies
shifting the whole population into a lower risk category benefits more individuals that shifting high risk individuals into a lower risk category as there are smaller numbers of them

What is the virtuous cycle of public health?
A complex chains of events that reinforce themselves through a feedback loop

What are the requirements for heath improvement?
- Resources
- Skills
- System Level Working (working together)

How can we understand health needs on a population level?
- Research
- Routine Data
- Health Needs Assessment
- Health equity audit
- Service improvement and evaluation
What is a logic model?
Logic models identify, describe and arrange the critical aspects of an intervention to represent how the intervention produces change

Give an example of an actual logic model used in the NHS.

What are some primordial and primary preventions for smoking?
- Laws
- Cost
- Packaging

What are some secondary preventions for smoking-related disease?
- Ask, Advice, Ask
- Screening

What are some population level screening programmes in the NHS?

What are some issues with evaluating the impact of health improvement initiatives?
- Might not predict certain outcomes so won’t measure them
- Some changes might take a long time to see
- Can be difficult to replicate findings from research studies into real world setting
What is lead time bias?
- Early diagnosis falsely appears to prolong survival
- Patients live same length of time but longer knowing they have the disease

What is length time bias?
- Screening programmes better at pick up slow growing less aggressive cases
- Diseases detectable through screening are more likely to have favourable diagnosis

What is social prescribing?

Who is often targeted in social prescribing?

What are some services available on social prescribing?
- Sports clubs
- Volunteering
- Religious groups
- Parks and outdoor spaces
- Community groups

What are the benefits of social prescribing?
- More holistic care
- Less GP appointments needed
- Clinicians can focus on medical issues
- More cost effective for GP practices
- Increases GP links with community services
What is the process of social prescribing?
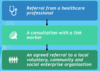
What are some social presriptions for social isolation?
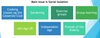
levels of intervention and examples

types of transmission

types of prevention

what is the definition of public health
the science and art of promoting and protecting health and wellbeing, preventing ill-health and prolonging life through the organised efforts of society
definition of population health
It is about improving the physical and mental health outcomes and wellbeing of people, whilst reducing health inequalities within and across a defined population








