3.1.3 Staphylococci Flashcards
(27 cards)
List general characteristics of bacteria in the genus Staphylococcus (gram, shape, arrangement, catalase status)
Gram +, cocci, clusters, catalase +
Staphylococcus is catalase ____ and oxidase ____
Positive, negative
What are some of the dz’s caused by staphylococcus?
1 cause of infective endocarditis, nosocomial bloodstream infections, and orthopedic ones
Septic shock mortality rate is high
What is the most virulent species of the Staphylococcus genus?
Staph. aureus
What do MSSA and MRSA stand for?
Methicillin-susceptible Staph. aureus
Methicillin-resistant Staph. aureus
Most MRSA infections in hospitals are typically acquired where?
CA-MRSA
What causes foodborne intoxication with staphylococcus?
Ingestion of heat-stable enterotoxin (transmitted by food handlers)
Describe the onset of food intoxication seen with staphylococcus
Rapid onset (within 1-6 h)
What are some of the clinical syndromes seen with Staph aureus?
LOL

What are the major virulence factors of S. aureus?
4 cytolysins
leukocidins
modulins
Enterotoxins
Adherence factors (Protein A, fibronectin-binding proteins, collagen-binding proteins)
Other secreted enzymes
What is the main type of infections is most common with S. aureus?
Skin/soft tissue infection (95%)
-cellulitis, impetigo, abcess/furuncle
What this be?

Abscess/furuncle
What is this? Which toxin is responsible?

Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSS) - Ritter’s syndrome
Exfoliative toxins ETA and ETB
What age group is most at risk for SSS?
Children under 5
This skin desquamation is a result of which toxin? What is the name of this syndrome?
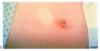
Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS) - shock w/n 48 hrs
Superantigen
What is the mechanism of TSST-1 toxin?
Binds T cell receptor and MHCII of APC => constituitively active
Leads to massive release of cytokines -> hypotension, shock, and death

Infection of bone or bone marrow

Osteomyelitis
What cardiac abnormality is associated with S. aureus?

What are some of the Respiratory tract infections associated with S. aureus?
Pneumonia, empyema, cystic fibrosis

What are the two topical rx options for S. aureus?
Bacitracin (MSSA > MRSA)
Mupirocin (MSSA and MRSA)
What are the different rx options for MSSA and MRSA?

What morphilogical change is associated with VISA? VRSA?
VISA (Vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus) - thickened cell wall
VRSA (Vancomycin-resistant S. aureus) - acquired resistance plasmid from Enterococci
What is the coagulase status of S. epidermidis?
Negative
What are some of the opportunistic infections of S. epidermidis?
Primary implant, catheter and prosthetic joints, bacteremia (biofilm)






