Lecture 7- Lumps and swellings of the oral cavity and lips Flashcards
What is this? What causes it?
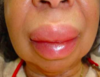
Angiodema- commonly caused by ace inhibitors
WHAT IS THIS?

Alergic cheltitis
What is this condition?

Erythema multiforme
What is OROFACIAL GRANULOMATOSIS? (OFG)
Chronic or recurrent swelling of the orofacial tissues with no evidence of gastrointestinal involvement. Can get mucosal tags Lip swelling Fissuring PERIVERMILLION ERYTHEMA Histopath shows non caseating granulomateous infammation Exclude the presence of fungi and mycobacteria swell as foreign material.
what are the differential diagnoses of OFG?
Oral Crohn’s MelkerssonRosenthalSyndrome(Orofacialswelling, fissured tongue, facial palsy) Sarcoidosis •Allergic causes eg. angioedema
Investigations of OFG?
orofacial signs may precede intestinal disease in 60% of cases exclude other diagnosis e.g sarcoidosis Biopsy and microscopic investigation OFG can be caused by allergy so may do allergy testing
How to manage OFG?
Topical and systemically.
Topical -intralesional steroids-(Triamcinolone Acetonide) - Topical steroids(Adcortyl in Orabase)
- Topical immunosuppresants (Protopic)
Systemic-
Steroids
- Antimicrobials (Dapsone)
- immunosuppressants (Azathiaprine)
How do you distinguish between crohns and OFG
Chrones has gut involvement but otherwise the facial symptoms are the same,
What oral symptoms are their of crohn’s?
Staghorning,
recurrent apthous ulcerations,
PYOSTOMATOTIS VEGETANS( specific marker for IBD)
What features does crohn’s show down the microscope?
Ulceration
Submucosal oedema and lymphangiectasia
Focal and diffuse lymphoid infiltration
Non-caseating epithelioid granulomas
Granulomatous lymphangiitis
How do you manage Crohn’s?
Management should be holistic.
Same topical and systemic considerations as OFG Anti TNF-alpha (infliximab)
what is sarcoidosis?
it is a Chronic multisystem disorder of unknown origin non caseating epithelioid granulomas.
It effects Lungs, liver, spleen, lymph nodes, skin, eyes and bone
What are the oral manifestations of sarcoidosis?
Lip swelling,
granular gingivitis tongue isn’t usually involved
Often involved the labial glands
What are the investigations for sarcoidosis?
- Biopsy
- Chest radiograph - bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy - pulmonary fibrosis
- Blood and urinary calcium
- Serum angiotensin converting enzyme
what can be the causes of localised intraoral swellings?
• Cystic • Neoplastic • Reactive • Inflammatory • Vascular • Developmental • Infective






