orofacial infections- fungal and bacteria Flashcards
what are the local predisposing factors to candida albicans?
Denture wearing at night
Dry mouth
Steroid therapy
High carb diet
what is the most common fungal infection in the mouth?
Candida
it is opputnistic and a commensal
what are the systemic factors which predispose you to candida infection?
immunocompromise
extremes of age
Antibiotic therapy
Diabetes mellitus
Anaemia
what are the acute types of oral candidosis?
acute pseudomembranous candidosis (thrush)
acute erythemateous candidosis
what are the chronic types of candidosis?
chronic hyperplastic candidosis (candidal leukoplakia)
chronic erythematous candidosis (denture stomatitus)
what are the candida associated lesions?
Candida associated chelitus
How do you diagnose candida?
Swab
How do you manage acute psudomembranous candida?
Address the predisposing factors
Always test FBC, Folate, Vit b and random blood glucose as fear may be diabetic.
Can be due to HIV but dont screen every patient.
What does thrush look like?
white patches on the mucosa which can be easily removed by wiping to leave and erythematous area underneath.
Can be asymptomastic or can cause soreness.
what is the treatment of thrush?
Topical antifungal therapy- Nystatin or miconazole
Systemic antifungal therapy- reserved for the immunocomprimised or those with servere systemic infection.
need to follow up- ensure that is has resolved.
manage risk factors
If got test results back
what is chronic hyperplastic leukplakia?
candidal leukoplakia
Non removal white lesions on the buccal mucosa
mostly bilateral and seen in smokers
what is acute erythemateous candidal infection?
acute atrophic candidosis
erythematous area
treat by correcting local and systemic factors often steroid inhaler use.
treat with topical antifungal
how do you manage chronic hyperplastic candidosis?
identify and correct local and systemic risk factors
Treat with topical antifungal - nystatin/miconazole
Systemic antifungal - fluconazole 50mg o.d for 14 days
Review due to malignancy risk
what is chronic erythematous candidosis?
Denture stomatitis
erythema is usually confined to teh hard palate under a denture area.
Often asymptomatic
Treatment is by a topical antifungal and modifying risk factors.
what is this?
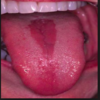
Median rhomboid glossitus ( it is a candida associated lesion)
Rhomboid region located in posterior 1/3rd anterior 2/3rd border
Topical therapy is sufficient


