4. Wavefunctions and orbitals Flashcards
(16 cards)
Explain the de Broglie equation
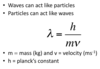
Explain the Heisenber Uncertainty Principle
Probability of finding an e at certain location
Principle states that the more precisely the position of some particle is determined, the less precisely its momentum (quantity of motion of a moving body, measured as a product of its mass and velocity) can be predicted from initial conditions, and vice versa

What is a wavefunction
Wavefunction (Ψ) - a mathematical description of a wave
- Schrodinger defined the wavefunction to describe an e
- Bohr interpreted Ψ2 as the probability of finding an e anywhere in a certain space
Explain Schrodingers equation
Used to find the allowed energy levels of quantum mechanical systems (such as atoms)
- time independent (this particular)
- H - Hamiltonian operator (representing the energy of the electrons and nuclei in a molecule)
- E - possible energies
- Ψ (psi) - wavefunction

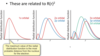
How are the Schrodinger and Bohr equations related?
The solution of H atom (two body system = e and proton) e to the Schrodinger matches the Bohr equation
- n - principal quantum number
- R - Rydberg constant
=> in H the E only depends on the quantum number
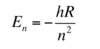
Which quantum numbers are used to characterise atomic orbitals?
For H:
- n: energy - can be any energy
- l: shape - can be any from 0 to n-1
l = 0 -> s
l = 1 -> p
l = 2 -> d
l = 3 -> f
- ml: orientation - can be any whole number from -l to +l (L not 1)

What are the two possible coordinate systems for describing atomic orbitals?

How is distance from the nucleus and the shape of the orbital noted?

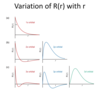
Explain R on R(r) graphs
Info on d_istribution of charge density inside an orbital_
Density as the distance from nucleus increases / amplitude of the wavefunction (???)
- 2s a point where equals 0 - a node (where R(r)=0) - the phase changes (from + to -)
- 3s - two nodes → 3 phases
- the more nodes → the higher the E
Explain radial distribution functions
Show the probability of finding an e at a cretain distance from the nucleus
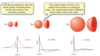
Explain the phase changes in 1s, 2s and 3s orbitals
- All s orbitals are spherical
- 1s no phase changes
- 2s on phase change (positive darker inside region, negative - lighter region)
- 3s → 2 phase changes (3 phases in total)
Explain the phases of p orbitals
- each lobe is a new phase - differently coloured (doesn’t matter which)
- 3 perpenticular orbitals (x, z, y)

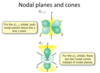
Explain nodal planes in p orbitals
- nodal planes - where the wavefunction is equal to 0

What are the shapes of d orbitals?
- x, y, z
- phases go: light, dark, light, dark (positive - negative phases)
- in dz2 3 orbitals - 2 merged

What are the nodal planes in d orbitals?
What is a phase of an orbital?
Positive
Negative



