Liver Nodules and Tumors Flashcards
What are the types of Nodular hyperplasia of the liver
1) focal
2) nodular regenerative hyperplasia
Describe focal nodular hyperplasia
these are well-demarcated but poorly encapsulated nodules that appear mostly as spontanoues mass lesions in an otherwise normal liver
Gross: central gray-white, depressed stellate scar from which fibrous septa radiate to the periphery.

When are focal nodular hyperplasia most common?
•most frequently in young to middle-aged adults.
Focal nodular hyperplasia has an association with _____
oral contraceptives
What is this showing?

focal nodular hyperplasia marked by:
Broad fibrous scar with hepatic arterial and bile duct elements
chronic inflammation present within parenchyma that lacks normal architecture due to hepatocyte regeneration.
What are the 3 classic histologic features of focal nodular hyperplasia?
abnormal architecture,
bile ductular proliferation,
malformed vessels

Describe nodular regenerative hyperplasia
•denotes a liver entirely transformed into nodules—grossly similar to micronodular cirrhosis—but without fibrosis.
Nodular regenerative hyperplasia can lead to what?
portal HTN
When does nodular regenerative hyperplasia typically occur?
Occurs in association with conditions affecting intrahepatic blood flow, including:
solid-organ (particularly renal) transplantation,
hematopoetic stem cell transplantation, and
vasculitis

What is this showing?

Nodular regenerative hyperplasia- Normally the liver cell plates (lined by dark‐staining reticulin fibers), should be of equal width—1 hepatocyte wide. In this photo there is a nodule in the center of the field in which the plates in the center of the nodule are wide and the plates at the edge are narrowed (arrows). This change, in the absence of significant fibrosis, is indicative of nodular regenerative hyperplasia.
Describe what is shown in this photo of nodular regenerative hyperplasia?

sinusoidal dilation (arrows).
NO inflammatory infiltrate or areas of necrosis.
The common factor in both types of hepatic nodular hyperplasia seems to be what?
either focal or diffuse alterations in hepatic blood supply, arising from obliteration of portal vein radicles and compensatory augmentation of arterial blood supply.
What is this showing?

Reticulin staining highlighting the nodular regenerative hyperplasia pattern- Atrophic hepatic cords on the left alternate with plump, thickened cords on the right.
What is this showing?

trichrome highlighting compressed central veins in nodular regenerative hyperplasia
What is the main benign neoplasm of the liver?
Cavernous hemangiomas
hepatocellular adenoma
What are the most common benign liver tumors?
Cavernous hemangiomas
What is this showing?
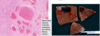
Cavernous hemangioma of the liver
Micro: Blood-filled vascular channels separated by a dense fibrous stroma.
Gross- discrete red-blue, soft nodules, usually less than 2 cm in diameter, generally located directly beneath the capsule
Describe hepatocellular adenomas and where they derive from
benign liver tumors developing from hepatocytes
What is this?

Hepatocellular Adenoma
What things are associated with the formation of hepatocellular adenomas?
oral contraceptives and anabolic steroids- Arises in normal or nearly normal liver in patients with abnormal hormonal or metabolic condition
How do hepatocellular adenomas appear histologically?
cords of hepatocytes, with an arterial vascular supply (arrow) and no portal tracts












