6 - ICH - Genetics & Inheritance Flashcards
(47 cards)
Define Genotype
Genotype = The genetic makeup of an organism and describes the organism in terms of the alleles it contains
Define Phenotype
Phenotype = Observable characteristics of an organism. It is the result of the interaction between the genotype and the environment which can modify the organism’s appearance
Define Gene
A DNA sequence that codes or a polypeptide
Define Allele
Different forms of the same gene
Define Homozygous and Heterozygous
Homozygous = Body cells in an organism have 2 identical alleles for a gene and all gametes carry the same allele
Heterozygous = Body cells in an organism have 2 different alleles for a gene and gametes will carry one copy of one of the alleles
Define
Dominant
Recessive
Co dominant/ incomplete dominance
Dominant = Allele if present will always be expressed in the phenotype
Recessive = Allele is only expressed in phenotype in the homozygouse state
Co dominant/ incomplete dominance = Both alleles are equally dominant and are both expressed in the phenotype
Define Locus
Locus = The specific position of a gene on a DNA molecules/ chromosome
What are genetic diagrams and their purpose?
Genetic diagrams show the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring that would be produced if two parents are crossed
What is monohybrid inheritance? + Example
Inheritance of a characteristic controlled by a single gene
- E.g. Tall/ short pea plants
What is another name given to monohybrid inheritance?
Monogenic inheritance
If 2 homozygous parents are crossed in a monogenic cross. What is expected of the genotypes of the F1 (first generation offspring)
They’ll all be heterozygous
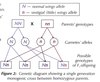
What is a phenotypic ratio?
Phenotypic ratio = The ratio of different phenotypes in the offspring
Name 3 different types of genetic cross diagrams you need to know + example of each
Monohybrid inheritance - Inheritance of 1 gene
- Tall/ short pea plants
Dihybrid inheritance - Inheritance of 2 genes
- Shape and colour of pea plants
Multiple allele inheritance
- Blood group
Why is blood group expressed as IA, IB and IO
What does the I stand for?
Immunoglobin
- How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have?
- What are autosomes and how many pairs do humans have?
- Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes
- Autosomes = pairs of chromosomes that are identical in appearance (humans have 22 pairs)
XY chromosomes for a male and female?
Female = XX
Male = XY
Can any gene on a sex chromosomes be sex-linked?
Yes
Can alleles be carried on the X and Y chromosome?
What is particular about the alleles expressed and the X chromosome?
Y = Carries no alleles
X = Carries a allele ∴ in males often when the allele on X is recessive it will still be expressed since there’s no allele on the Y chromosome
Draw a genetic cross diagram to illustrate the inheritance of sex
Monohybrid cross diagram

What a gene being called sex-linked mean?
Sex-linked = The allele is carried on either the X or Y chromosome but in practise very few is carried on the Y chromosome (we assume none for genetic crosses)
If a genetic disease is carried on the X chromosome what sex has a greater predisposition for the disease? Why?
Males, because the Y chromosome doesn’t really carry any alleles (assume none in questions) ∴ the allele carried on the X chromosome regardless of whether it is recessive or dominant will be expressed
Name 2 diseases that are sex linked
- Is the faulty allele dominnt or recessive
- What sex has a greater predisposition for the disease?
- Haemophilia and red/ green colour blindness
- Alleles responsible for these diseases are recessive
What is haemophilia
Condition in which the blood does not clot, leading to slow and persistent bleeding, especially into joints
What is red green colour blindness?
Difficulty distinguishing between red and green.
Gene controlling red green colour vision is located on the X chromosome









