exam 2 circulatory Flashcards
When pressure applied to this accumulation of fluid and this dent pushes fluid into the adjacent area this is an example of ___

pitting edema
Name this type of edema and in what body cavity is it?

hydrothorax in the thoracic cavity
Mulberry dz is characterized by this type of fluid accumulation with fibrin cloudy strands

pericardial effusion
This dog with CHF has ascites/ hydroperitoneum which consits of exudate or transudate?

transudate
This horse with CHF has what occuring in its peritoneal cavity?

ascites
Generalized edema with profuse accumulation of fluid within the subcutaneous tissue

anasarca
submandibular edema is commonly called
bottle jaw
horse has generalized edema from

protein loosing enteropathy
This lung histology characterizes _____ because of the accumulation of pink tinged fluid

pulmonary edema
Left sided CHF along with thickened alveolar walls and the infiltration of alveolar macrophages indicates an acute or chronic pulmonary edema?
chronic
What are these in the lungs?

Hemosiderin-laden Macrophages* (“heart failure cells”)
This increase of blood vol/flow in the arterial side of the capilary bed
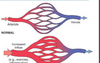
hyperemia
This increase in blood vol/flow on the venous side of the capillary bed?

congestion
itis indicates?
inflammation
true or flase
The twisting of vessels in a gastric volvolus intitally leads to hyperemia.

false
congestion
What is the pathogenisis of this intestinal volvulus

Twisting of vessels obstructs intestinal veins → severe venous congestion (acute, local, congestion) → ischemia (necrosis) →loss of endothelial integrity →hemorrhage →shock →death
Acute pulmonary congestion is usually associated with what other pathological process in response to L CHF

pulmonary edema
This diffuse brownish discoloration of the lungs is attributed to what 2 processes

chronic pulmonary edema/ ocngestion due to L CHF

























