wk 2 - Gluconeogenesis & General Regulatory Mechanisms COPY Flashcards
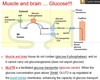
In Cori Cycle, lactate is produced in the ———– (organ) and it is converted to ———- (carbohydrate).
In Cori Cycle, lactate is produced in the liver and it is converted to glucose.
10?
(pathway)

lipolysis
(triacylglycerols/fatty acids are broken down via beta oxidation to produce acetyl coa molecules & glycerol)
Glycerol is mostly found in the adipose tissue (subcutaneous), it goes to the —-where it gets converted to —-, which can be used as a fuel in other tissues.
a) Adipose tissue
b) Muscle
c) Liver
d) Glucose
e) Glycogen
Glycerol is mostly found in the adipose tissue (subcutaneous), it goes to the liver where it gets converted to glucose, which can be used as a fuel in other tissues.

Which 3 reactions during glycolysis are irreversible during gluconeogenesis?
a) Step 1, 8 & 10
b) Step 1, 3 & 10
c) Step 1-3
d) Step 8-10
b) Steps 1, 3 & 10
(3 kinases)
S1 - hexokinase requires 2 ATP
S3 - PFK-1 requires 2 ATP
S10 - pyruvate kinase requires 4 ATP

The liver itself can’t use the ketone bodies as a source of energy as it lacks the enzyme ____ ________ ___ ________, also called _________, that is responsible for producing acetyl CoA from the ketone bodies.
The liver itself can’t use the ketone bodies as a source of energy as it lacks the enzyme β-ketoacyl-CoA transferase, also called thiophorase, that is responsible for producing acetyl CoA from the ketone bodies.

during starvation, in what order are the following molecules utilised as fuel?
- proteins (muscle)
- ketones
- glucose
- fatty acids + minimal proteins
- glycogen
- Glucose
- Glycogen
- Fatty acids + minimal protein
- Ketones
- Proteins (muscle)
…then death

during starvation, the human body’s first priority is to:
provide sufficient glucose to brain and other tissues that are dependent on it (Figure A)

8?
(pathway)

glycolysis - TCA cycle
pyruvate is sent from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria via pyruvate translocase, and is then converted to acetyl CoA via pyruvate deydrogenase complex (PDH) to enter the TCA cycle
________ is an important product for the synthesis of ATP and citrate via the Krebs Cycle. It is produced from:
- fatty acids (during beta oxidation - lipolysis)
- glucose (end product of glycolysis)
- amino acids (during Cahill cycle)
- ketone bodies (precursor for ketogenesis)
- oxaloacetate (during Gluconeogenesis)
- and ethanol (via ADH)
Acetyl CoA

If acetyl CoA is the precursor for production of energy via TCA cycle, what is the purpose of converting acetyl CoA by the liver mitochondria to ketone bodies, then re-converting ketone bodies to acetyl CoA in the tissues?
ketone bodies are water soluble and can be transported from the liver to other tissues easily without the need of albumin or lipoproteins as carriers.

In the human body, which fuel store can last for the longest time?
adipose fat
Lymphatic cells absorb and transport fatty acids and lipids as _____ from the digestive system
Lymphatic cells absorb and transport fatty acids and lipids as lymph from the digestive system
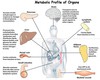
When _________ stores are depleted, the liver is able to synthesize glucose from lactate, via ___________

When Glycogen stores are depleted, the liver is able to synthesize glucose from lactate, via gluconeogenesis
13?
(pathway)

ketogenesis
acetyl CoA is used to make ketone bodies - betahydroxybutyrate & acetoacetate
A ketogenic amino acid can be degraded directly into ________, which is the precursor of ketone bodies
A ketogenic amino acid can be degraded directly into acetyl-CoA, which is the precursor of ketone bodies

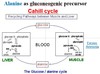
When do muscle cells use the Cahill cycle and not the Cori-cycle?
When the muscles need to get rid of ——-
a) Ammonia
b) Oxaloacetate
c) Water
d) Lactic acid
a) Ammonia

In the Cahill cycle, pyruvate is converted to alanine in muscle cells, then to glucose in the liver when there is a need to transfer ammonia to the liver.
Compartmentation is the seperation of ________ and _________ pathways
Compartmentation is the seperation of synthesis and degradation pathways

What is the main hormone secreted to reduce the blood glucose level?
a) Glucagon
b) Growth hormone
c) Insulin
d) Oestrogen
c) Insulin
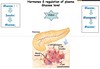
Glycolysis produces —– ATP, whereas, gluconeogenesis consumes —- ATP.
Glycolysis produces 2 ATP, whereas, gluconeogenesis consumes 6 ATP.
Glycogen is formed from ——, which is glycolysed to —-, then to —–, then getting stored in ——— as glycogen.
a) Adipose tissues and liver
b) Glucose
c) Glucose-1-phosphate
d) Glucose-6-phosphate
e) Muscle and liver
Glycogen is formed from Glucose, which is glycolysed to Glucose-6-phosphate then to Glucose-1-phosphate, then getting stored in Muscle and liver as glycogen.

The glycogen stored in muscle is made accessible to be used by other organs.
a) True
b) False
b) False

- Only the glycogen stored in the liver can be made accessible
to other organs.
The Cori cycle (lactate to glucose) normally accounts for 20% of glucose turnover, but it was shown to be increased to 50% in ————— patients.
a) Arthritis
b) Cachectic cancer
c) Cirrhosis
d) Diabetic
e) Glucoma
The Cori cycle (lactate to glucose) normally accounts for 20% of glucose turnover, but it was shown to be increased to 50% in Cachectic cancer patients.
(Cachexia is characterized by loss of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle mass - wasting syndrome)

ethanol is primarily metabolised by the liver, converted to ___________ by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) which takes place in the cytoplasm. This toxic product is then converted to ______ by aldehyde dehydrogenase
(some is metabolised in the stomach - the stomach lining contains ADH)
ethanol is primarily metabolised by the liver, converted to acetaldehyde by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) which takes place in the cytoplasm. This toxic product is then converted to the relatively inert acetate by aldehyde dehydrogenase
(some is metabolised in the stomach - the stomach lining contains ADH)

GLUT2 is a facilitated glucose transporter (glucose carrier). When the glucose concentration goes above 30mM, GLUT2 is up-regulated at the _____ _______ ________, enhancing the capacity of glucose transport
GLUT2 is a facilitated glucose transporter (glucose carrier). When the glucose concentration goes above 30mM, GLUT2 is up-regulated at the brush border membrane, enhancing the capacity of glucose transport.

——— is characterized by loss of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle mass.
Cachexia is characterized by loss of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle mass.
19?
(pathway)

glycolysis
the _____ _____ ____ carries nutrients from the intestine to the liver
the hepatic portal vein carries nutrients from the intestine to the liver

name the 5 amino acids that are exclusively glucogenic:
- Threonine
- Tyrosine
- Isoleucine
- Phenylalanine
- Tryptophan
(T, Y, I, F, W)

Alanine, glycerol and lactate are precursors of gluconeogenesis. Where can you find them in the body?
- alanine - from muscle
- glycerol - from adipose tissue
- lactate - from muscle, RBC’s, via the cori cycle

12?
(pathway)

HMG CoA reductase, can be either:
- melvanoate pathway (for cholesterol synthesis)
- or ketogenesis
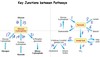
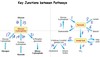
Oxaloacetate has the choice to be converted to —- (gluconeogenesis) if the human body ——- to use energy (ATP) or to —– (glycolysis) if the human body —— energy (ATP)
a) Acetyl CoA & citric acid
b) Lactate or ethanol
c) Needs
d) Doesn’t need
Oxaloacetate has the choice to be converted to lactate or ethanol (gluconeogenesis) if the human body doesnt need to use energy (ATP) or to Acetyl CoA & citric acid (glycolysis) if the human body needs energy (ATP)
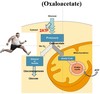
What will happen to your body’s glycogen stores during fasting? Why?
glycogenolysis, conversion of glycogen to glucose for energy to supply plasma glucose to tissues (brain, RBC, testes, renal mediulla & embryonic tissues)

Fasting requires all the glucose to be synthesized from ———— precursors
Fasting requires all the glucose to be synthesized from gluconeogenesis precursors
What is the starting material for gluconeogenesis?
a) Amino acids
b) Fats
c) Lipids
d) Oxaloacetate
d) Oxaloacetate

Why it is recommended to eat while you drink alcohol?
a) Because ethanol makes you feel hungry
b) Because ethanol produces low concentration of NADH, which inhibits glycogenesis (supress glycogen production and cause hypoglycaemia)
c) Because ethanol produces high concentration of NADH, which inhibits gluconeogenesis (supress glucose production and cause hypoglycaemia)
d) Because ethanol produces high concentration of NADH, which inhibits glycogenesis (supress glycogen production)
c) Because ethanol produces high concentration of NADH, which inhibits gluconeogenesis (supress glucose production and cause hypoglycaemia)

which fuel is preferred by skeletal and heart muscle at times of rest:
Fatty acids
(aerobic environment)
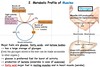
ATP is released in —— and it is consumed in ——.
a) Glycolysis
b) Gluconeogenesis
ATP is released in Glycolysis and it is consumed in Gluconeogenesis.
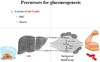
What is the end product of glycogen in muscles during exercise?
a) Acetate
b) Amino acids
c) Glucose
d) Lactate
e) Ketonic bodies
d) Lactate
- exercise changes the cell to an anaerobic environment (from depleted O2 due to an increased cellular respiration rate) = fermentation of pyruvate to produce lactate

In the human body, which fuel store is the largest?
a) Adipose fat
b) Liver glycogen
c) Muscle glycogen
d) Muscle protein
d) Muscle protein

Although costly in Phosphate bonds (net 4), the ____ ____ allows the organism to accommodate to large fluctuations in energy needs of skeletal muscle between rest and exercise
Although costly in Phosphate bonds (net 4), the cori cycle allows the organism to accommodate to large fluctuations in energy needs of skeletal muscle between rest and exercise

What is the fuel of the brain in case of starvation?
a) Glucose
b) Glycogen
c) Glucose 6-phosphate
d) Ketone bodies
e) Starch
d) Ketone bodies
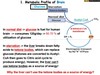
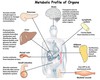
Which organ does all the following?
- Synthesises glucose
- Stores glycogen
- Produces ATP
- Secrets wastes
- Provides fuel to brain, muscle and other organs
liver

In a starvation state, once TAG stores are depleted, ______ degradation accelerates which will eventually lead to death due to loss of heart, liver, and kidney function
In a starvation state, once TAG stores are depleted, protein degradation accelerates which will eventually lead to death due to loss of heart, liver, and kidney function

After 40 days of starvation, the brain gets ___% of its energy from ketone bodies
After 40 days of starvation, the brain gets 70% of its energy from ketone bodies

_________ _______ uses ATP to do mechanical work
skeletal muscle uses ATP to do mechanical work
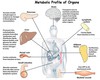
In glucose synthesis from glucose-6-phosphate, glucose 6-phosphatase is activated by ———– (metal cation)
Mg2+
The process whereby precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids are converted to glucose is termed ___________
Gluconeogenesis
What is the main hormone secreted to increase the blood glucose level?
a) Glucagon
b) Growth hormone
c) Insulin
d) Oestrogen
a) Glucagon
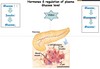
Where in body you can find mostly triacylglycerol?
adipose tissues
the _____ processes fats, CHO’s and proteins from the diet, synthesises ans distributes lipids, ketone bodies and glucose for other tissues & converts excess nitrogen (ammonia) to urea.
the liver processes fats, CHO’s and proteins from the diet, synthesises ans distributes lipids, ketone bodies and glucose for other tissues & converts excess nitrogen (ammonia) to urea.

Acetone, acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate are classified as ——-
ketone bodies
In the Cahill Cycle, blood transfers glucose from —–
a) Liver to muscle
b) Muscle to liver
c) Muscle to pancreas
d) Pancreas to liver
a) Liver to muscle
21?
(pathway)

Pentose phosphate pathway
Gluconeogenesis costs __ ATP to produce one glucose molecule

Gluconeogenesis costs 6 ATP to produce one glucose molecule
In humans, two amino acids are exclusively ketogenic:
Lysine & Isoleucine
the human body has ‘reserves’ for starvation for ___-___ months, however our glucose reserves are exhausted after ___ day/s
the human body has ‘reserves’ for starvation for 1 - 3 months, however our glucose reserves are exhausted after 1 day

In glucose synthesis from glucose-6-phosphate, glucose 6-phosphatase is activated by:
a) Ca++
b) Mg++
c) Na+
d) K+
b) Mg++

for the average person (70kg), liver glycogen lasts approximately __ hours
for the average person (70kg), liver glycogen lasts approximately 3 hours

Ethanol consumption leads to an accumulation of NADH, which leads to what 3 metabolic factors:
- inhibits gluconeogenesis (prevent oxidation of lactate to pyruvate) -> lactate accumulates
- inhibits fatty acid oxidation -> stimulates fatty acid synthesis in liver -> TAG accumulates -> fatty liver
- block the processing of acetyl-CoA by citric acid cycle, thus ketone bodies were generated in blood and pH drops.

during starvation, the human body’s second priority after providing sufficient glucose to the brain, is to:
preserve protein by shifting from utilization of glucose to utilization of fatty acids + ketone bodies
(Figure B)

In acid-base homeostasis, ketone bodies can cause ——–
Metabolic acidosis
(ketoacidosis)
What is the organ that consumes most glucose in the body?
a) Brain
b) Kidney
c) Liver
d) Lung
e) Pancreas
a) Brain

What is the net cost of phosphate in Cori Cycle?
4 pi
What are the dangers for other organs (excluding the brain) to use ketone bodies during a prolonged starvation state?
Ketone bodies are acidic = decreases blood pH = enzymes may not be able to function optimally (enzyme inhibition)

Glucose 6-phosphate is catalyzed with glucose 6-phosphatase yielding ——-
a) Fructose
b) Fructose 6-phosphate
c) Glucose
d) Glycogen
e) Lactose
c) Glucose

Glycogen is broken-down in the muscles to glucose-6-phosphate (G-6-P). However, G-6-P can’t be converted to glucose in the muscles due to lack of the enzyme ——–.
glucose-6-phosphatase
what 3 pathways are inhibited during a fed state?
Inhibition of:
- Gluconeogenesis
- Glycogenolysis
- Lipolysis

during a starvation state (hypoglycaemia), fatty acids can be oxidised to produce _____ ____ via lipolysis (beta oxidation), which is then sent to the _____ mitochondria to be converted into ______ ______ .
Because these are water soluble, they can be easily transported from the liver to other tissues to be re-converted to _____ ____ for energy production (TCA cycle)
during a starvation state (hypoglycaemia), fatty acids can be oxidised to produce Acetyl CoA via lipolysis (beta oxidation), which is then sent to the liver mitochondria to be converted into ketone bodies.
Because these are water soluble, they can be easily transported from the liver to other tissues to be re-converted to Acetyl CoA for energy production (via TCA cycle)

2?

Fructose 6-phosphate
up arrow = Gluconeogenesis,
down arrow = glycolysis

1?

Glucose 1-phosphate
(Glycogenolysis)

Gluconeogenesis releases energy, whereas glycolysis consumes energy.
a) True
b) False
a) False
gluconeogenesis consumes energy (endergonic)
glycolysis releases energy (exergonic - 96.2 kJ/mol)

Irreversible reactions during glycolysis must be bypassed during ———-
a) Hydrolysis
b) Gluconeogenesis
c) Glycogenesis
d) Phosphorylation
b) Gluconeogenesis

How does the human body regulate/inhibit glycolysis?
Once the human body has enough ATP (glycolysis pathway is no longer needed), the produced ATP will allosterically inhibit the enzymes responsible in glycolysis in step 1 (Hexokinase), step 3 (Phosphofructokinase/PFK-1) and step 10 (Pyruvate kinase) and thus saves the energy consumed in these steps

Which organ has the most important site for gluconeogenesis during starvation?
a) Brain
b) Kidney
c) Liver
d) Lung
e) Muscles
kidney
(provides 50% of blood glucose via GNG)

Which hormone do you expect to function in case of high concentration of plasma glucose? What do you call this process?
a) Glucagon, glycolysis
b) Glucagon, gluconeogenesis
c) Insulin, glycolysis
d) Insulin, gluconeogenesis
c) Insulin, glycolysis

Which organ has the most important site for gluconeogenesis during starvation?
kidneys
Brain and muscles don’t have glucose-6-phosphatase and accordingly they can’t synthesize glucose.
a) True
b) False
a) True

in the cori cycle, Lactate produced from ______ passes via the blood to the liver, where it may be converted to _______
in the cori cycle, Lactate produced from pyruvate passes via the blood to the liver, where it may be converted to glucose

Insulin stimulates all the following Except:
a) Gluconeogenesis
b) Glycogenesis
c) Glycolysis
d) Lipogenesis
e) Protein synthesis
a) Gluconeogenesis
(only catabolic pathway, insulin is anabolic)

8 - 24 hours without food is called the ____ ______ state
8 - 24 hours without food is called the early fasting state

The process whereby precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, and amino acids are converted to glucose is termed
a) Glycolysis
b) Glycogenesis
c) Glycogenolysis
d) Gluconeogenesis
d) Gluconeogenesis

During gluconeogenesis,
Glycogen is stored in——-
a) Brain and spleen
b) Liver and muscle
c) Liver and spleen
d) Pancreas and spleen
b) Liver and muscle

During glycolysis, step 1 & 3 lose __ ATP (1 ATP each), whereas step 10 makes __ ATP, so the overall will be ___ ATP
During glycolysis, step 1 & 3 lose 2 ATP (1 ATP each), whereas step 10 makes 4 ATP, so the overall (net) will be 2 ATP