83 + 84 CNS Tumors Flashcards
(53 cards)
Gliomas
- What are the three types of glioma classes?

Astrocytoma
- How common are these?
- What time of life do they occur?
- Where do they usually occur in the brain?
- What are the 3 most common presenting signs/symptoms?

Astrocytomas
- What are the 3 groups of astrocytomas, based on histological features?

Astrocytoma
- What kind is shown?

A fibrillary astrocytoma, WHO grade II, with mildly pleomorphic astrocytes with minimally increased cellularity is shown
Astrocytoma
- What kind is shown?

An anaplastic astrocytoma, WHO grade III, with increased cellularity, nuclear pleomorphism and a mitotic figure in the center of the field
Astrocytoma
- What kind is shown?
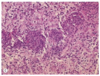
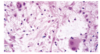
Glioblastoma multiforme, WHO grade IV, with prominent microvascular proliferation
Astrocytoma
- What kind is shown?

Glioblastoma multiforme, WHO grade IV, with significant nuclear pleomorphism and hyperchromaticity and a central focus of tumor cell necrosis
Astrocytoma
- Diffuse astrocytomas
- How long do these remain static?
- What is the mean survival time?
- What happens to patients as the disease progresses?
- What is notable about the prognosis when histologic features start to show?

Astrocytomas
- What is notable about the gross morphological features of grade II and grade III astrocytomas?

Astrocytomas
- What is notable about the gross morphological features of multiforme glioblastomas?

Astrocytomas
- Diffuse Astrocytomas, Grade II
- What are the 3 characteristics for these?
- What is notable about the transition b/w neoplastic and normal tissue?

Astrocytomas
- Anaplastic Astrocytomas, Grade III
- What are the 2 notable features about the regions that have anaplastic astrocytomas?
- What type of figures are present?

Astrocytomas
- Glioblastoma
- What are the 2 histologic features that separate this from anaplastic astrocytomas?

Astrocytomas
- Brainstem Gliomas
- When do these occur?
- How common are these?
- What are the 3 types?
- How aggressive are the three types?
- When do these occur?

Oligodendrogliomas
- How common are these, relative to other gliomas?
- When do they occur in life?
- Where do they usually occur in the brain?
- What are the 2 main types, and what is the prognosis like for each?

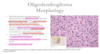
Oligodendrogliomas
- Grade II WHO, well differentiated
- What do these look like, grossly?
- Microscopically
- What do the nuclei look like?
- What does the cytoplasm look like?
- What is notable about the blood supply?
- What is notable about calcifications`?
Oligodendrogliomas
- Who is notable about anaplastic oligodendrogliomas (grade III), compared to grade II ones?

Gliomas
- Genetics
- What is the common mutation associated in grade II astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas?
- What mutation gives glioblastomas and other astrocytes immortality?
- What genes are deleted in many oligodendrogliomas?
- What mutations are seen in CNS tumors that are also seen in tumors outside the CNS?

Astrocytomas
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma
- How aggressive are these?
- Who do they affect?
- Why would a patient have neurologic symptoms after incomplete resection of this tumor?

Astrocytoma
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma
- What often accompanies these tumors?

Astrocytoma
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma
- What shape do these cells have?
- What substance do they test positive for?
- What kind of fibers are often present?
- What shape do these cells have?

Astrocytoma
- Pilpcytic Astrocytoma
- Genetics
- How is the MAPK signalling pathway actiated?
- Genetics

Ependymomas
- What time of life do they usually occur?
- Where in the brain do these usually arise, relative to the age of patients?
- Which age/area is related to neurofibromatosis type 2?
- What area has good prognosis?

Ependymomas
- What do these tumors look like when they occur in the 4th ventricle?