Behavioral Sciences 8: Social Processes, Attitudes, and Behavior Flashcards
social action
actions and behaviors that individuals are conscious of and performing because others are around
social facilitation
people tend to perform better on simple tasks when in the presence of others
people naturally exhibit a performance response when they know they are being watched
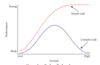
Yerkes-Dodson law of social facilitation
being in the presence of others will enhance the ability to perform tasks that one is already good at (simple tasks) and will hinder the performance of less familiar tasks (complex tasks)
deindividuation
a loss of self-awareness in large groups, which can lead to drastic changes in behavior (antinormative behavior)
bystander effect
when in a group, individuals are less likely to respond to a person in need
social loafing
the tendency of individuals to put in less effort when in a group setting than individually
peer pressure
social influence placed on an individual by a group of people or another individual
peers
individuals who are equals within a social group
identity shift effect
- individual’s state of harmony disrupted by a threat of social rejection, and individual conforms to group norms
- individual will begin to experience internal conflict because the behavior is outside the normal character of the individual
- individual adopts the standards of the group as her own
cognitive dissonance
the simultaneous presence of two opposing thoughts or opinions
social interaction
how two or more individuals can both shape each other’s behavior
group polarization
the tendency for groups to make decisions that are more extreme than the individual ideas and inclinations of the members within that group
individuals in group situations will form opinions that are more extreme than they would if making the decision alone (choice shift - doesn’t always have to be negative)
groupthink
desire for harmony or conformity results in a group of people coming to an incorrect or decision
consensus decisions are reached without discussions of alternatives
illusion of invulnerability
factor indicative of groupthink
the creation of optimisim and encouragement of risk-taking
collective rationalization
factor indicative of groupthink
ignoring warnings against the ideas of the group
illusion of morality
factor indicative of groupthink
the belief that the group’s decisions are morally correct
excessive stereotyping
factor indicative of groupthink
the construction of stereotypes against outside opinions
pressure for conformity
factor indicative of groupthink
the pressure put on anyone in the group who expresses opinions against the group
viewing the opposition as disloyal
self-censorship
factor indicative of groupthink
the withholding of opposing views
illusion of unanimity
factor indicative of groupthink
the false sense of agreement within the group
mindguards
factor indicative of groupthink
the appointment of members to the role of protecting against opposing views
fad
behavior transiently (briefly) seen viewed as popular and desirable by a large commmunity
mass hysteria
a shared, intense concern about the threats to society
culture
the beliefs, behaviors, actions, and characteristics of a group or society of people
- learned by living in the society and adopting their practices
- passed on between generations
culture shock
cultural differences seen when traveling outside of one’s own society
assimilation
process by which an individual’s or group’s behavior and culture begin to resemble that of another group
blending of new aspects of a society with old ones, changing the culture itself - melting pot
multiculturalism
communities or societies containing multiple cultures - cultural mosaic
subcultures
groups of people within a culture that distinguish themselves from the primary culture to which they belong

