Test 2 - Nucleoside (Corrected) Flashcards
Nucleoside
Nitrogenous base + sugar
Nucleotide
Phosphate added. to nitrogenous base and sugar
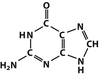
Purines
Adenine and Guanine Built in steps onto PRPP
Pyrimidines
Cytosine and Thymine Completed pyrimidine ring is added to PRPP
Purine Synthesis First Commited Step?
- The donation of an amino group from Glutamine to PRPP. Adds amino group to C1, and removes phosphate group. (Highly unstable).
- Regulated by negative feedback of IMP, AMP, and GMP.
- Allosteric inhibition by ADP and GDP.
Difference between Synthase and a Synthatase?
- Synthatases: use ATP or GTP
- Used in de novo synthesis.
- Synthase: do not
What is the End Stage of De novo Purine Synthesis?
- Inosinate (IMP)
- Hypoxanthine is the base on this molecue.
- Last common step between AMP and GMP.
- Can then be converted into AMP or GMP.
- AMP and GMP inhibit their own synthesis.
- Hypoxanthine is the base on this molecue.
AMP and GMP synthesis
- They regulate one another. This prevents too much of one being made.
- GTP is required to make AMP
- ATP is required to make GMP.
Broad Stroaks of de novo Purine synthesis.
- Ribose 5-phosphate to PRPP
- Catalyzed by: PRPP synthetase
- Inhibited by ADP
- Catalyzed by: PRPP synthetase
- PRPP to 5-phospho-ribosyl-amine
- Catalyzed by Glutamine giving amine group
- Inhibited by AMP, GMP, IMP
- Catalyzed by Glutamine giving amine group
- 5 - phosphoribosylamine to IMP
- Divergence
- AMP production
- IMP to Adenylosuccinate
- Inhibited by AMP
- Adenylosuccinate to AMP
- IMP to Adenylosuccinate
- GMP production
- IMP to XMP
- Inhibited by GMP
- XMP to GMP
- IMP to XMP
- AMP production
de novo Pyrimidine Biosynthesis First commited step?
- Is the combining of carbamoyl phosphate with aspartate.
- Allosterically hindered by CTP.
Unlike purine biosynthesis ______ is the precursor to the other pyrimidines?
and it is formed into what?
Uridylate (UMP)
Formed into a Triphosphate (UTP) prior to conversion.
Feedback regulation of pyrimidine biosynthesis?
CTP inhibits synthesis
ATP + CTP results in almost normal activity but still less than normal rate.
Where do the nucleoside monophosphates (NMP) get their phosphates?
- ATP donates
- Catalyzed by each NMPs respective kinase
- Eg. Adenylate kinase for AMP.
- Sugar doesnt matter deoxy or ribo.
- Catalyzed by each NMPs respective kinase
Gout cause and treatment
- During purine degradation
- AMP and GMP converted to Xanthine
- Xanthine to Uric Acid
- Catalyzed by Xanthine oxidase
- Inhibited by Allopurinol
- A build up of uric acid causes Gout
- Catalyzed by Xanthine oxidase
Cause of Bubble people
- During Purine degradation
- AMP to Adenosine
- Adenosine to Inosine
- Catalyzed by Adenosine Deaminase (ADA)
- A deficiency in ADA results in 100 fold increase in dATP which results in defects in T and B lymphocyte development.
- Catalyzed by Adenosine Deaminase (ADA)