Histology of the GI Tract Flashcards
What are the layers of GI tube?

- Mucosa ( epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mocusae)
- Submucosa
- Muscularis externa (Inner circular muscle, and outer longtidunal muscle)
- Adventitia/ Sarosa

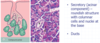
Mucous secreting cells of the Stomach are found where?
Found on the surface on the epithelium
How does cells secreting mucous appear on when stained? Identify them on the image?
Pale, because their cytoplasma is filled with mucous.
The pale top surface are single cells that produce mucous and bicarbonate

What is the classification of the epithelium in th eoesophagus?
Pluse
Label the image? identifying the mucusa, submucosa, musclaris externa, sorasa/adventitia. Also Identify epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mocusae…ect
Stratified squamous non-keritinised epithelium

What do parietal (oxyntic) cells secrete? Identify them? describe them

Hydrochloric acid
description: large pale pink stained, with spherical nucleus

What do chief (peptic) cells secrete? identify?
Pepsinogen (precurser for pepsin, conveted into pepsin upon contact with HCL acid)
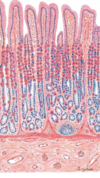
What is the classification of the epithelium in the stomach?
Simple columnar epithelium
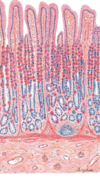
In what layer are the gastric glands in the stomach found?
Mucosa (above muscularis mucosae)

What is unique about the Stomach Layers ? what does the gastric pits open to?
Mucosa – is folded into Rugae.
- Empithelium – is simple columnar + dipressions called gastric pits.
- The Lamina Propria —- is Gastric Glands
- Muscularis Mocusae—nothing especial (same)
Submucosa —-same
Muscularis externa
- inner most oblique
- inner circular
- outer longtidunal
Sarosa..why
***** Gastric pits open to the gastric glands*****

What is found in the mucosa of the small intestine?
Villi
Crypts of Leiberkuhn
Lymphoid aggregations (Peyer’s patches)

Where are Brunner’s glands found? Identify them on the image?
Submucosa of the duodenum
Brunner’s glands secrete alkalin substance to neuturalis the acid from the stomach

In what part of the GI tract are peyer’s patches found? identify them?

more in the Ileum, some in duodanum.
Identify the Peyer’s patch, and all other structrures in the duodanum on the Q section?

What are the classic histological feature of the ileum?
label the image
lots of payer’s patch and villi

What part of the GI tract is the following image? features?

Jejunum
Jejunum: is do not have Brunner’s gland or Peyer’s patchs ( you maight see one or payer’s patch but not alot)
Jejunum have the classic mucosa, submucosa, musclaris externa, and sarosa/ adventitia.
What part of the GI tract is the following image?

Duodenum