Abdomen: Viscera Flashcards
(71 cards)
Innervation of peritoneum
Parietal: spinal somatic fibres: localised pain
Visceral: visceral afferents: referred pain
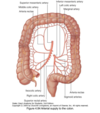
Greater sac and lesser sac (omental bursa)
Greater sac contains most of the abdomen
Lesser sac: posterior to stomach and liver
Omental epiploic foramen
Joins lesser sac to greater sac

Structures anterior to omental (epiploic) foramen
Portal vein
Hepatic artery proper
Bile duct

Structures posterior to epiploic foramen
inferior vena cava
Structures inferior to epiploic foraman
1st part of duodenum
Structures superior to epiploic foraman
caudate lobe of liver

Greater omentum
Greater curvature of stomach
Drapes down anterior to transverse colon, ileum and jejunum
Loops back up and joins transverse colon peritoneum
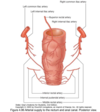
Lesser omentum
Lesser curvature of stomach to inferior liver

Mesenteries
Mesentery Proper (connect small bowel to posterior abdo wall)
Transverse mesocolon (connect transverse colon to posterior abdo wall)
Sigmoid mesocolon (connect sigmoid colon to posterior abdo wall)
https://www.tiktok.com/@guidedbiology/video/7267238841533091115

Mesentery Proper
The only double layered fold of peritoneum
connects jejunum and ileum to posterior wall

Structures entering through the diaphragm
Vena cava + right phrenic T8 [Audi Slogan - VoRsprung durch T8nik]
Oesophagus + vagus T10 [OVO]
Aorta + thoracic duct T12 [12 letters in thoracic duct]
Blood supply to abdominal oesophagus
Left gastric artery
Inferior phrenic artery
Different parts of stomach
Note: cardial notch: superior angle where oesophagus enters stomach
Angular incisure: bend on lesser curvature
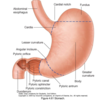
Arterial supply of stomach
Left gastric (branch of coeliac trunk)
Short gastric (originate from splenic artery which is a branch of the coeliac trunk)
Gastro-epiploic arcade (vascular network formed by left and right gastroepiploic arteries along greater curvature of stomach)
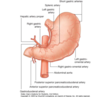
Parts of duodenum
Superior
Descending
Inferior
Ascending

Duodenum intra or extraperitoneal
First part: intra peritoneal
Rest: extra peritoneal
Blood supply to duodenum
Superior and inferior pancreatoduodenal arteries

Difference between the appearance of ileum and jejunum

Jejunum:
- longer vasa recta, smaller arcade
- Larger calibre.
- Darker
- less mesenteric fat
- Deeper valvulae conniventes
Ilieum:
- smaller vasa recta, more developed arcade.

Source of bleeding from a deudonal ulcer
Posterior wall
Pancreatodeudonal artery
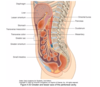
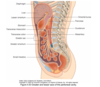
Different positions of appendix
Retrocaecal 74%
Pelvic 21%
Pre and Postileal
Sub and Paracaecal

Identification of appendix during surgery
Caecal taenia coli converge at base of appendix and form a longitudinal muscle cover over the appendix.

Blood supply to appendix
Appendicular artery (branch of ileo-colic artery)

Colon, intra or retroperitoneal
Appendix and caecum: intra
Ascending: retro
Transverse: intra
Descending: retro
Sigmoid: intra
Rectum: (distally) retro