Advanced True Learn #2 Flashcards
(229 cards)
Hoow do gabapentoids create relief on a molecular level?
The gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin) result in a
- Decreased release of glutamate*, *norepinephrine*, and *substance P (all chemicals that are considered pronociceptive) via their binding to voltage-gated calcium channels within the central nervous system.

The most common cause of death from subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) within the first 24 hours?
Rebleeding (Peaks at 24 hours)
When does vasospasm events occur most commonly after SAH?
Vasospasm typically develops by the third day and peaks within 5-10 days, resolve over 10-14 days
2/3 of SAH patients vasospasm
What blood product should be used to minimize dilutional coagulopathy?
Fresh frozen plasma should be used to reduce the risk of dilutional coagulopathy during massive transfusion.
With obstructive disease, who responds the most to bronchodilator therapy?
Moderate disease
Healthy, severe, and mild disease = Mild Response to bronchodilators
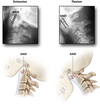
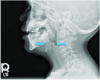
The most common cause of sudden stridor 24 to 96 hours post thyroidectomy is what?
The most common cause of sudden stridor 24 to 96 hours post thyroidectomy is hypocalcemia.
Post Op Thyroidectomy
Stridor and difficulty with phonation.
Diagnosis?
Damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve is more likely to cause early stridor and difficulty with phonation.
Post Op Thyroidectomy
Change in Pitch of Voice noted on extubation
Diagnosis?
Damage to the superior laryngeal nerve would cause a change in the pitch of the patient’s voice as the superior laryngeal nerve innervates the cricothyroid muscle.
Why does phosphorous and glucose levels drop with TPN?
Total parenteral nutrition carries a significant glucose load that increases the pancreatic secretion of insulin.
Insulin causes several metabolic effects, including the cellular uptake of glucose and phosphate
What are 3 scenarios that low phosphate levels are encountered?
- Refeeding syndrome
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Large decreases in PCO2 (e.g., hyperventilation during hypercarbic respiratory failure)
What is Refeeeding Syndrome?
Refeeding syndrome is a term that refers to various metabolic abnormalities that may complicate carbohydrate administration in subnourished patient populations.
Refeeding syndrome (a constellation of fluid and electrolyte disorders, most notably severe hypophosphatemia) after starting TPN occurs frequently in patients who have had poor or no nutritional intake for >72-96 hours. Patients at high risk for refeeding syndrome also have reduced levels of prealbumin (< 10 mg/dL).
Hypophosphatemia is the most well known, and perhaps most significant, element of the refeeding syndrome, and may result in sudden death, rhabdomyolysis, red cell dysfunction, and respiratory insufficiency.
Hypokalemic periodic paralysis:
Inheritance pattern?
What channel is affected?
Hypokalemic periodic paralysis is a rare autosomal dominant disorder resulting in an abnormal dihydropyridine sensitive calcium channel

Gastroschis vs. Omphalocele
Which is more common?
The incidence of gastroschisis is 0.4-3 per 10,000 births, compared to the more common omphalocele, occurring in 1.5-3 per 10,000 births
What is the Pentalogy of Cantrell?
1) Omphalocele
2) Ectopia cordis (heart partially or completely outside thorax)
3) Ventricular septal defect or ventricular diverticula
4) Sternal cleft
5) Anterior diaphragmatic hernia

What is the best test for carcinoid syndrome diagnosis?
urine 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid. (Urine 5-HIAA)

What is the formula for determining how much sodium bicarbonate to give?
Initial sodium bicarbonate (mEq) =
[0.3 * patient weight (kg) * (24 – patient HCO3 mEq/L)]/2
OR
The amount of sodium bicarbonate that will normalize the pH in most patients can be approximated using the formula:
Sodium bicarbonate (mEq) = 0.2 * (kg) * base deficit
Butorphanol mechanism?
Butorphanol is a mixed opioid agonist-antagonist with partial agonism of the mu and kappa opioid receptors.
If it is used with opioid full agonists, the partial agonist properties of butorphanol will behave as an antagonist. The effect of butorphanol leads to pain relief but does not lower the seizure threshold.
What are the absolute contraindications to ECT?
pheochromocytoma
Recent stroke
Recent intracranial surgery
Intracranial mass lesion
Recent MI
Unstable cervical spine
What physiological changes are seen in ECT?
The first 5-10 second tonic phase of the seizure is characterized by parasympathetic activity with bradycardia and hypotension.
The second clonic phase of the seizure lasts up to 10 minutes and is characterized by sympathetic activation with hypertension and tachycardia.
How soon do you have to wait after an MI to have ECT?
American College of Cardiology-American Heart Associate guidelines suggest a 4-6 week delay in elective surgery, such as ECT, after an uncomplicated myocardial infarction
What is the osmolarity difference of LR and Plasmalyte?
The osmolarity of Plasmalyte is 294 mOsm/L, which is iso-osmolar compared to the lactated Ringer solution, which is hypoosmolar (273 mOsm/L).
How do you identify the Lateral Femoral Cutaneous nerve by landmark technique?
The LFCN may be anesthetized by injecting local anesthetic:
2-2.5 cm medial and 2-2.5 cm inferior to the ASIS and above and below the fascia lata.

What position do you put the patient should you suspect you have an air lock on TEE for Venous Air Embolism?
Left Lateral Decubitus Position

Place surgical site below heart (if able)
Lower the head position & compress the jugular veins (if surgical site above the neck)
Reposition the patient into left lateral decubitus, trendelenberg, or left lateral decubitus head down position (controversial - poor evidence & often impractical to do in the OR)
What are the benefits to adding Epinephrine in Locals Anesthetics?
- Increases the block duration and intensity
- Decreases systemic absorption due to its vasoconstrictive properties
- Direct analgesia via its α2-adrenergic agonist properties