Aldehydes & Ketones Flashcards
(15 cards)
what is the systematic naming system for aldehydes?
replace the -e on the corresponding alkane with -al for aldehydes.

what is the naming system for ketones?
Replace th -e on the corresponding alkane with -one for ketone.

what are the special chareacteristics about the carbonyl functional groups of aldehydes and ketones?
1) it has a planar sterochemistry
2) the oxygen on the carbonyl is partilal negative( undergoes electrophilic addittion at the oxygen)
3) the carbon on the carbonyl is partial positive(will undergo nucleophilic addition at the carbon atom)
4) they have higher boiling points than corresponding alkanes
5) they cannot hydrogen bon with each other(boiling point is lower than alcohols), but can hydrogen bond with water and amines
6) they are soluble in water up to four carbons
How are the carbons named?
The carbon next to the carbonyl group is called the alpha carbon. The carbon next to the alpha is called the beta carbon. and the carbon next to the beta carbon is the gamma carbon.

which hydrogen is the most acidic in carbonyl molecules ond why?
The alpha carbon which is secondary hydrogens are more acidic. The alpha carbons that has an carbonyl groip on both sides is the most acidic.
The more carbonyl groups increases the resonance stabilization.

What is a tautomer?
what is Keto-enol tautermerization?
A tautomer are isomers that differ by the position of the alpha hydrogen. Keto-enol tautomerization is when a ketone exist in eqtilibrium with a double bond between the carbonyl carbon and the alpha carbon. the alpha carbon has been moved to the oxygen molecule and made into an alcohol. All ketones xist this way at equillibrium but the ketone dominates.

what are the effect of elctronwithdrawing/donating groups on the reactons of ketones and aldehydes?
Withdrawing groups incease the positive character of the carbonyl carbon making it more attractive to nucleophiles. Thus increasing the reaction.
Donating decreases the positive character. This makes the carbonyl less positive slowing down the reaction.
Which is more easily oxidized aldehydes or ketones?
aldehydes. Ketones are rarely oxidized.
Name some reactions of aldehydes and ketone ?
1) reduction by a reducing agent to alcohols and grignards
2) oxidation to carboxyilic acid from aldehydes
3) hemiacetal/hemiketal formation
4) acetal/ketal formation
Explain the mecahnism of hemiacetals/hemiketals in terms starting/ending intermediate and catalyst.
Aldehydes and ketones first form a hemiacetal when reacted with alcohol and aqqueous acid catalyst. the ROH group is added to the carbonyl carbon. this is called a nucleophollic addition. the acetal is formed with the addition of the same ROH group.

explain the mechanism of formation of an Imine (schiff base).
Imine formation happens between the nucleophilic addition on a primary amine of to the carbonyl carbon. What is left is a double bond between the carbonyl carbon and the nitrigen group with the R group attached to the nitrogen. The oxygen is leaves as water.

Explain the formation of an enamine.
formation of a enamine happens between a Ketone or aldehyde with a secondary amine. a double bond forms between the carbonyl carbon and the alpha carbon. A single bond forms between the amine and the and the carbonyl carbon.
*tertiary amines do not react
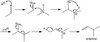
explain the aldol condensation.
a base catalyzed reaction of aldehydes and ketones. the alpha carbon of one foems a bond with he carbonyl group of the other . the carbonyl is then converted into a alcohol. the intermediate is a aldol (alcohol and aldehyde).
the aldol undergo a condesation which leaves a double bond between the alpha and beta carbon. this is called a enal(alkene and aldehyde)
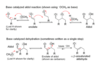
what are the properties of a alpha-beta unsaturated carbonyl?
On the alpha beta conjugated carbonyl a nucleophile is extremely attracted to the beta carbon. This breaks the bond between the alpha and beta carbon and adds a nucleophile to the beta carbon.

Explain the Wittig reaction.
In the witting reaction an ylide converts a ketone into a alkene.



