Anatomy Flashcards
(87 cards)
The hip joint
ASIS - anterior superior iliac spine

Knee bones

Ankle bones

Inguinal ring borders

Saphenofemoral junction
2.5cm below and lateral to the pubic tubercle
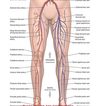
Quadricep Muscles
Rectus femoris
vastus lateralis
vastes medialis
vastus intermedius
hamstrings
biceps femoris
semitendinosus
semimembrinosus
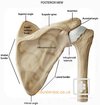
shoudler joint
Calf
Gastrocnemius - lateral epicondyle
subclavian steal
narrow proximal subclavian artery (proximal to where vertebral artery leaves)
decreased pressure distally
:. subclavian artery takes blood from contralateral vertebral artery (via circle of willis and back down the vertebral artery)
can steal from internal mammary - CABG
lehriche
aortoiliac occlusion
absent femorals
buttock claudication
erectile dysfunction
gunstock deformity
malunion of a spuracondylar fracture
wedge osteotomy of lateral humerus
mitral regurgitation
jet width 0.6cm+
regurgitant volume more than 60 ml
aortic stenosis
pressure gradiant >40
valve area <1cm^2
6 Ps
acute limb ischaemia
pulseless
painful
Pallor
perishingly cold
paraesthesia
paralysis
Still’s
juvenila idiopathic arthritis
salmon coloured rash comes and goes
mig infuinal point scar
Navy
nerve
artery
vein
y fronts - lateral to medial
Posterior cruciate ligament anatomy
lateral edge of medial femoral condyle
tibial plateau
anterior cruciate ligament
posterior to anterior
lateral to medial
superior to inferior
attachments -
- notch of distal femur (lateral femoral condyle)
- tibial plateau
Acromegaly management
ocreotide - somatostatin analogue
pegvisomant - GH antagonist
examine
hands
face
visual fields - bitemporal hemianopia
Graves
carbimazole
propilthyouracil
radioiodine
Dercum’s
adiposis dolorosa
multiple painful benign lipomas
in obese
ICD
implanatable cardioverter defribrillator
Shoulders