Anatomy - Back, Lymphatics and Nerves cont. Flashcards
(68 cards)
location of lamina on vertebra
between spinous and transverse processes

location of pedicle on lamina
between vertebral body and articular facet

label this vertebra


intervertebral notch/foramen
gap between two vertebrae where spinal nerves pass through
type of joint between vertebral bodies
secondary cartilagenous/
fibrocartilagenous/ synphysis joint
(the intervertebral disk forms the fibrous cartilage part of the joint)
type of joints between articular facets of ajacent vertebrae
synovial plane
how many cervical vertebrae are there?
7
how many thoracic vertebrae are there?
12
how many lumbar vertebrae are there?
5
how many sacral vertebrae are there?
5
how many coccygeal vertebrae are there?
4
name given to C1
altals
name given to C2
Axis
name given to C7
vertebra prominens
describe a cervical vertebra
very small transverse process,
small body
split spinous process
large vertebral cannal
foramen for vertebral artery and veins to pass through

describe a thoracic vertebra
long transverse processes
downward pointing spinous process
medium body
small/low articular facets

describe a lumbar vertebra
short transverse processes
large body
long spinous process
high articular facets

annulus fibrosis
outer fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc

nucleus pulposus
inner gel like centre of the intervertebral disc
“slipped disk”
the nucleus pulposus herniates (protrudes) through the annulus fibrosis. can be serious of it herniates posterolaterally and compresses an emerging spinal nerve.
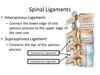
ligamenta flava
(singular. ligamentum flavum)
connect adjacent vertebral laminae from C2 to S1

anterior longitudinal ligament
runs down the anterior surface of the spine.
crosses all the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs.
prevents hyperextension

posterior longitudinal ligament
on the posterior surfaces of the vertebral bodies (inside the vertebral canal)
from C2 - S1
prevents extreme flexion

supraspinous ligament
connects the tips of the spinous processes from C7 to S1
limits hyperflexion of the vertebral column