Anatomy: Brain and Cranial Nerves Flashcards
(83 cards)
name this part

subarachnoid space
name the regions


which of the following is correct for nerve modalaties:
CN IX
somatic sensory
somatic motor
special sensory
mixed
parasympathetic
Mixed (s motor, s sensory, special sensory, parasympathetic)
Leaves cranial cavity via jugular foramen
Sensory function: innervates oropharynx, carotid body and sinus, posterior 1/3 of tongue, middle ear cavity
Special sensory function: provides taste sensation to the posterior 1/3 of tongue
Parasympathetic function: of parotid gland
Motor function: innervation of the pharynx
which of the following is correct for nerve modalaties:
CN IV
somatic sensory
somatic motor
special sensory
mixed
parasympathetic
somatic motor
Leaves cranial cavity via superior orbital fissure
(function: movement of eye)
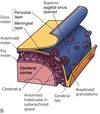
what is the middle layer of the meninges called
arachnoid mater

what is the function of the pia mater
coats the brain and blood vessels
(nerves entering and leaving the brain)
identify the cranial nerve

facial nerve
CN VII
identify the cranial nerve

Optic nerve
CN II
name the marked features

3rd ventricle
4th ventricle
spinal canal filled with CSF
whats the difference between sensory and special sensory
Special senses detect the sensations of taste, smell, hearing, equilibrium, and sight, and are linked to a specific organ (sight = eyes)
name this part of the sinus

confluence of sinuses
what is the function of arachnoid mater
arachnoid mater contains arachonid granulation, which reabsorb spinal fluid
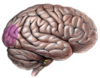
in which lobe would you expect to find visual processing
occipital lobe
what artery branches of the basilar artery, before the basilar artery diverge to form the communicating artery,
right and left posterior cerebral artery

what is produced in the 1 and 2 ventricles

cerebral spinal fluid
how do sympathetic nerve fibres reach the orbit.
by following arteries, especially the internal carotid artery
name the foramens present in the middle cranial fossa

- Optic canal
- Superior orbital fissure
- Foramen rotundum
- Foramen ovale
- Foramen spinosum
- Carotid canal
identify the marked structures

red = optic chiasma
blue = pituitary stalk
where does venous blood from here drain to

superior sagital sinus

which of the following is correct for nerve modalaties:
CN XII
somatic sensory
somatic motor
special sensory
mixed
parasympathetic
motor
Leaves cranial cavity via the hypoglossal canal,
motor function of the tongue.
describe what is happening in the image

as the sinus makes its way down inferiorly, it passes through the jugular foramen.
once passed it becomes the right internal jugular vein
identify the cranial nerve

olfactory
CNI
which cranial nerve passes through the purple structure

Olfactory nerve
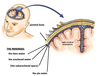
When the periosteal and meningeal layer of the dura mater seperate, what does this form?
dural venous sinuses