Anatomy of the hand and wrist (clinical relevance) Flashcards
(16 cards)
What names are given to each finger?
Thumb - D1
Index - D2
Long - D3
Ring - D4
Little - D5
Name the corresponding hand bone groups
How many carpal bones are there?

8 carpal bones

Name the joints that exist between bones in the hand
How many of each are there?
Names of joints are just the two bone groups mashed into one.
4x Distal interphalangeal joints (DIP)
4x Proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints
1x Interphalangeal (IP) joint (in the thumb)
5x Metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints
5x Carpometacarpal (CMC) joints
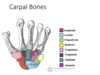
Name each of the carpal bones

The important ones are the:
- Scaphoid
- Trapezium
- Lunate
What is the clinical relevance of the blood supply to the scaphoid bone?
The scaphoid bone has a retrograde blood supply (ie blood vessels to it go backwards) from the radial artery
When fractured - the proximal end of the scaphoid (which is at the end of the blood vessels) is liable to avascular necrosis
The more proximal the fracture - the more likely AVN

What is the anatomical snuffbox?
What is it’s clinical relevance?
Triangular area of the hand between the Extensor pollicis longus (EPL), Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) and the abductor pollicis longus (AP)
You can palpate the scaphoid through this deepening - which means in scaphoid fractures, palpation causes pain to the patient

What can be palpated in the anatomical snuffbox?
Radial artery
Radial styloid process
Scaphoid
Trapezium
Base of the 1st metacarpal
Name the superficial flexors of the fingers (that are on the forearm)
Pronator teres - Index finger
Flexor carpi radialis - Middle finger
Palmaris longus - Ring finger (missing on some people)
Flexor carpi ulnaris - Little finger
PFPF
Identify the superficial flexors of the forearm?


What two flexor tendons are attached to the fingers?
Flexor digitorum superficialis
Flexor digitorum profundus

How would you test to see if there is damage to the flexor digitorum profundus?
The FDP is the only tendon that acts on the Distal interphalangeal joint
(as it attaches to the distal phalanx)
To test - isolate the distal phalanx (DIPJ) and ask to flex

How would you test the Flexor digitorum superficialis?
To test the FDS of a finger - you must straighten out the surrounding fingers by holding them down
This is to isolate the FDS and remove any input from the FDP
This is because the FDP has a shared muscle belly with the other FDPs of other fingers

The extensors of the wrist are all covered by the Retinaculum
What is the retinaculum attached to?
Triquetrum & the Pisiform
Carpals^
The blood supply to the hand revolves around a Superficial arch and a deep arch
What arteries supply each of these structures?
Superficial arch - Ulnar artery
Deep arch - Radial artery
what gives rise to the common digital arteries?
These come off the Superficial arch of the hand
Therefore the Ulnar artery supplies the common digital arteries
NOte that some people don’t have an ulnar artery
How do you test to make sure a patient has both Radial artery and ulnar artery supply to their hand
Allens test:
- Occlude radial & ulnar arteries at the wrist
- Patient closes hand into fist and holds
- Patient opens hand - release Ulnar artery
- Watch if volar surface becomes pink again
If not then only the radial artery exists



