Anatomy: Overview of the Lower Limb Flashcards
(108 cards)
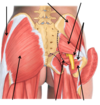

what are the superficial gluteal muscles
gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fascia latae
what are the superficial muscles of the gluteal region innervated by
gluteal nerves:
gluteal maximum: inferior gluteal
all other: superior gluteal
what are the deep muscles of the gluteal region innervated by
nerves from the sacral plexus
what is the function to the superficial muscles of the gluteal region
extensors (gluteus maximus)
abductors and medial rotators of thigh(gluteus med and min)
what is the function of the deep muscles of the gluteal region
-lateral rotators of thigh and hip stabilisers
Trendelenburg’s gait
when the pelvis drops on opposite side of the raised limb - indicates that the abductor muscles on the standing limb are weakened or paralysed (superficial muscles)
due to lesion in sup gluteal nerve


what quarter of the gluteal region would you use for injections
lateral upper
what are the greater and lesser sciatic foramens formed by
sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments
what forms the sciatic nerves
L4-S3
what forms the pudendal nerves
S2-S4
what forms the -Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh
S1-S3
what is the principal nerve to the perineum
pudendal nerve
what is the largest nerve in the body
sciatic (L4-S3)
what does the posterior cuatenous nerve of the thigh supply
skin over posterior thigh, popliteal fossa, lateral perineum and upper medial thigh
the sciatic nerve


where does the sciatic nerve usually exit
inferior to piriformis

what does the sciatic nerve supply in the gluteal region
nothing
what 2 nerves does the sciatic nerve consist of
tibial nerve and common fibular bunched together - separate in distal posterior thigh
what is the superior boundary of the femoral triangle
inguinal ligament
what is the medial border of the femoral triangle
lateral border of the adductor longus
what is the lateral border of the femoral triangle
medial broder of the sartorius
what forms the floor of the femoral triangle
iliopsoas laterally and pectineus medially














































