AS/AD Flashcards
(17 cards)
aggregate demand
- sum of planned consumption in an economy in a given period
- looks the same as normal demand curve
aggregate supply
sum of planned production in an economy in a given period
Keynesian vs. Neoclassical aggregate supply curves
a) Keynsian
b) Neo-classical

What does YFE refer to?
full employment level of output of a nation
Full employment level of output
- level of output of goods and services achieved when a nation is producing at or near its potential by employing all available land, labor and capital
- on its PPC
- low unemployment rate
- stable price level
How do these shift AD?
- interest rates increase
- income tax rates increase
- government expenditure increase
- consumer confidence improves
- business confidence improves
- expectation of future inflation
- expectation of future increased income/wealth
- expectation of future increased revenue/profit
- increase in foreign RGDP
- appreciation in value of domestic currency
- increase in foreign inflation rate

- left
- left
- right
- right
- right
- right
- right
- right
- left
- left
- right
How do these shift SR/LR AS?
- increase spending on education/training
- increase spending on capital spending
- increase spending on infrastructure
- decrease spending on research/development
- increase taxes on business earnings
- strengthen competition/anti-monopoly
- privatise state-owned assets
- strengthen union power
- decrease minimum wage
- increase transfer payments
- decrease training schemes
- increase marginal tax rate
- decrease capital gains tax
- weaken environment laws
- strengthen health/safety laws
- increase productivity
- increase wages
- increase cost of labor
- decrease cost of raw materials
- increase capital stock
- decrease cost of imported factors of production
- improvements in technology
- increase in budget deficit (crowding out)
- right (LR/SR)
- right (LR/SR)
- right (LR/SR)
- left (LR/SR)
- left (SR)
- right (SR)
- right (SR)
- left (SR)
- right (SR)
- left (SR)
- left (LR/SR)
- left (SR)
- right (SR)
- right (SR)
- left (SR)
- right (LR/SR)
- left (SR)
- left (SR)
- right (SR)
- right (LR/SR)
- right (SR)
- right (LR/SR)
- left (SR)
exogenous factors
out of control of policy makers
infrastructure
network of communication, transport, water, education, health, etc.
marginal tax rate
tax on money made from buying shares
capital gains tax
tax on profit from the sale of property or investment
What is the heuristic when determining short-run vs. short-run and long-run aggregate supply shifts?
- SR: costs of factors of production
- LR/SR: changes in quality or quantity of factors of production
marginal efficiency of capital graph
- only buy capital when money it makes > putting money in the bank
- changes in interest rates influence investment

loanable funds graph
- when government borrowing increases, crowds out private sector borrowing
- Keynes argues government borrowing only crowds out when AS is in vertical portion

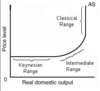
Keynesian aggregate supply
Keynesian range:
- recession - economy not fixing itself
- growth without inflation because no many unused factors of production
Intermediate range:
- inflation begins
- bottleneck: constraints on available, unused factors of production
classical range:
- inflation without growth
- demand-pull inflation - as AD shifts pulls up inflation
- businesses stealing factors of production from each other
- on PPC
Supply-side aggregate supply
- can briefly go beyond LRAS (not limit) but pulled back
- if AD grows, SRAS decreases as cost of production increases
- demand-pull inflation
- government intervention useless because pulled back
- believe economy always close to full capacity

inflationary and deflationary gap
- graph shows deflationary gap (inflationary is on other side)
- ‘close’ inflationary gaps
- ‘fill’ deflationary gaps
- inflationary gap: amount by which SRAS exceeds LRAS
- deflationary gap: amount by which LRAS exceeds SRAS



