Back and Spinal Cord Flashcards
(27 cards)
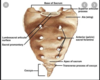
trapezius muscle location
attachments of trapezius muscle
Actions of trapezius muscle
anatomical relationships of trapezius muscle
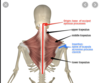
latissimus dorsi location
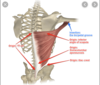
attachments of latissimus dorsi
functions of latissimus dorsi
innervation of latissimus dorsi
blood supply of latissimus dorsi
anatomical relationships of latissimus dorsi
clinical considerations of latissimus dorsi
triangle of auscultation
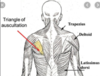
clinical significance of triangle of auscultation
The triangle of auscultation is a region of the posterior thorax devoid of superficial back muscles, which allows for optimal auscultating lung sounds.
inferior lumbar triangle

clinical significance of inferior lumbar triangle
The inferior lumbar triangle is a region of the lower back devoid of superficial back muscles, which is mildly susceptible to herniation (protrusion of tissue or organs).
borders of inferior lumbar triangle
Laterally: External oblique m.,
Medially: Latissimus dorsi m., &
Inferiorly: Iliac crest.
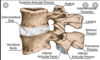
vertebral details

components of vertebral arch
- laminae
- pedicles
intervertebral foramen
The space between the superior articular process and the body is the superior vertebral notch, whereas the space between the inferior articular process and the body is the inferior vertebral notch. A pair of superior and inferior vertebral notches together form an intervertebral foramen, which is a lateral opening from the vertebral canal through which a spinal nerve is transmitted.
vertebral foramen

C1 (Atlas)
- The first cervical vertebrae, C1 (Atlas), forms that atlanto-occipital joint with the occipital condyles of the occipital bone of the skull. The atlas is unique among vertebrae in that it lacks a body.

C2 (Axis)
The second cervical vertebra, C2 (Axis), forms the atlanto-axial joint with C1. The dens is unique to the axis, and provides a pivot, about which the atlas may partially rotate.
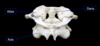
sacrum
In adults, the sacrum is composed of five fused vertebrae (S1-S5) of decreasing size. This bone articulates with the hip (coxal) bones at the sacro-iliac (S1) joints (laterally), the 5th lumbar vertebra (superiorly), and the coccyx (inferiorly)

coccyx
In adults, the coccyx is composed of four, fused, and rudimentary vertebrae (Co1-Co4) of decreasing size. This bone is colloquially referred to as the tailbone.