Basic Microscopy and Histology Flashcards
(62 cards)
How are stratified epithelia named?
According to the cells at its apical surface
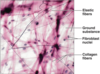
Areolar tissue contains multiple cell types including _________ and ________, and it includes ________, ________, and _______ fibers.
Fibroblasts
Macrophages
Elastic
Collagen
Reticular
What are the two major cell types of the nervous system?
Neurons, neuroglia
Identify letter n.

Fibroblast
What type of tissue and class is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, blood
Description: RBC and WBC in plasma matrix
Location: Blood vessels (Gas, nutrient, waste transport)
How are epithelial tissues classified on the basis of cell shape?
Squamous, cuboidal, and columnar
What are the three subtypes of loose connective tissue?
Areolar, adiose, and reticularis
What type of tissue, class, and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, dense, regular
Description: Primarily collagen fibers in parallel where fibroblasts are the major cell type
Location: Tendons, ligaments (Muscle attachment to bone or other muscle, tensile stress resistance when pulled in one direction)
Reticular tissue contains ________ cells and a network of _________ fibers.
Retricular
Reticular
What is the ground substance of blood?
Plasma
Cartilage contains _____% water
80
What do we mean by polarity?
Epithelial tissue has an apical (environment-facing) and a basal (internal-facing) side
What type of tissue, class, and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, dense, irregular
Description: Irregularly arranged collagen fibers where fibroblast is the major cell type
Location: Skin dermis, digestive tract submucosa (structural strength, tensile strength resistance in all directions)
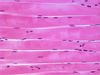
What type of tissue and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Muscle, smooth
Description: Spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei with no striations, arranged in sheets
Location: Walls of hollow organs (propulsion, involuntary control)
What occurs prior to microscopic examination?
Tissues are fixed, sectioned, and stained
What are the primary components of the neuon?
The soma (cell body), the dendrites, and the nerve fiber (axon)
What type of tissue, class, and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, cartilage, elastic
Description: Similar to hyaline cartilage but contains more elastic fibers in matrix
Location: External ear, epiglottis (shape maintenance, great flexibility)
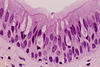
What is this tissue type? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Transitional epithelium
Description: Several cell layers that resembles stratified squamous or cuboidal with apical cells dome-liked or squamous-like depending upon degree of stretch
Location: Urinary bladder (stretch, distention)
What is this tissue type? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Simple columnar epithelium
Description: A single layer of tall cells with round-to-oval nuclei located at the base of the cell and some cells bear cilia
Location: Digestive tract (absorption and secretion; ciliated types propel mucus)
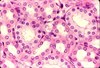
What type of tissue, class, and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, cartilage, hyaline
Description: Firm matrix produced by chondrocytes with mature chondrocytes in the lacunae
Location: Cartilage in nose, trachae, and larynx (support and reinforcement, resiliant cushioning, compressive stress resistance)
What tissue type is this?
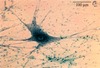
Nervous, neuron
What type of tissue and class is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, bone
Description: Hard, calcified matrix with many collagen fibers and osteocytes lie in lacunae
Location: Bone (support, protection, muscle lever, blood cell production)
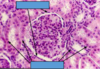
What type of tissue type and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Muscle, cardiac
Description: Cells are branched, lightly striated, and uninucleated, joined by intercalcated discs that may not be visible
Location: Walls of heart (blood circulation)
What are the three subtypes of cartilage?
Hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage