Block 2 Flashcards
(314 cards)
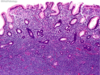
The esophagus has what type of epithelium?
Stratified nonkeratinizing squamous
The stomach has what type of epithelium?
simple columnar epithelium
The ___ junction is defined as the point where rugal folds stop between the stomach and the esophagus
gastroesophageal junction (GEJ)
The ____ junction is defined as the mucosal junction between the stomach and the esophagus.
Also called the ___ line
Squamocolumnar junction (SCJ)
Z line
If the gastroesophageal junction and the squamocolumnar junction (Z line) so not occur at the same level, what disease may be present?
Columnar metaplasia –> Barrett’s esophagus
The respiratory system develops as a diverticulum on the ventral surface of the gut tube at the level of the ___ pharyngeal arch.
This diverticulum is called the ___ ___. Divides in the midline to create the lung buds.
4th
Laryngotracheal groove
Esophageal atresia (which normally occurs as proximal atresia with distal fistula to the trachea) results in ____ in the fetus, because the fetus is unable to swallow amniotic fluid.
The blind esophageal pouch may hypertrophy and compress/thin the trachea, called ____.
polyhydramnios
Tracheomalacia
infant presents immediately after food with choking or vomiting when feeding. Dx and what other abnormalities may be present?
Esophageal atresia
VACTERL: Vertebral anomalies, anal atresia, cardiac defects, tracheoesophageal fistula, renal defects, and limb defects
Alternatively, TACRD: tracheal agenesis/atresia, cardiac abnormalities, radial ray defects, duodenal atresia
Non-circumferential, thin pieces of tissue in the mid or proximal esophagus. Can be congenital or acquired, such as in iron-deficiency anemia (Plummer-Vinson Syndrome)
Mucosal webs
Circumferential, thick rings of tissue in the distal esophagus. Associated with hiatal hernia
Schatzki rings
Dx?
Esophageal, mucosal webs
Iron-deficiency anemia
Glossitis
Cheilosis
Dysphagia
Plummer-Vinson Syndrome
An outpouching of the esophageal wall above the upper esophageal sphincter, which tightens abnormally instead of relaxing when swallowing.
Food may collect, causing halitosis, regurgitation, extrinsic obstruction, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Reflects underlying motor dysfunction.
Esophageal/Zenker diverticulum
List a few causes of extrinsic esophageal obstruction
Mediastinal masses
Vascular compression (aortic aneurysm, etc)
Surgical changes (herniation, fibrosis)
Degeneration of the ganglion cells in the myenteric plexus of the esophagus.
Can be primary (at birth) or acquired (Chagas disease, diabetes, autoimmune).
The inability of the LES to relax after swallowing and lack of peristalsis. Results in periodic obstruction and eventual dilation proximally.
Dysphagia, odynophagia, regurgitation, and increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Achalasia
A 40-yo physician returns from a trip with Doctors Without Borders in South America for 10 years. He suffers from dysphagia and weight loss over the last six months.
Achalasia secondary to Chagas disease
A patient presents with acute profuse bleeding following a night out drinking and vomiting this morning.
Mallory-Weiss tear at GEJ
A patient presents with acute profuse bleeding following a night out drinking and vomiting this morning. He suddenly develops trouble breathing and tachycardia.
Boerhaave’s Syndrome
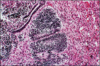
An immunocompromised patient presents with an esophageal infection that stains as pseudohyphae.
Esophageal candidiasis
An immunosuppressed patient presents with an ulcerated esophagus. Ground glass intranuclear inclusions appear when cells from the periphery of the ulcers are placed on slides.
Herpes simplex esophagitis
An immunosuppressed patient presents with an ulcerated esophagus. Intranuclear and intracytoplasmic inclusions are visible when cells from the base of the ulcer are placed on slides.
Cytomegalovirus esophagitis
Patient presents with dysphagia and a feeling of food in the bottom of his throat. He has a 30 year history of excessive drinking and often eats acidic or fatty foods.
GERD
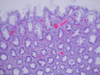
Dx?

GERD
erosive esophagitis seen as vertical linear streaks in the superficial mucosa
Top picture is normal. Dx the bottom picture.

GERD
Less surface maturation, basal cell hyperplasia, increases lamina propria inflammation, and papillae elongation
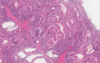
Columnar metaplasia with the addition of goblet cells can be defined as ____.
Intestinal metaplasia