Block 3 - CNS Flashcards
(113 cards)
___ aggregates are seen in Alzheimer’s, Pick disease, and progressive supranuclear palsy
Microtubule associated protein
Soluble in monomeric form
Insoluble fibrillary aggregates escape degradation and form neurofibrillary tangles
In some patients, the enzyme that cleaves the protein can be altered ( familial AD and PD)
tau
___ aggregates seen in Parkinson’s, dementia with lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy
synuclein
____ aggregates seen in Alzheimer’s and cerebral amyloid angiopathy
beta-amyloid
___ protein aggregates seen in CJD, vCJD, FFI, and animal diseases
prion
Type of degeneration seen in alzheimer’s
diffuse cortical
type of degeneration seen in diffuse lewy body disease
diffuse cortical
degeneration seen in frontotemperol dementias
diffuse cortical
type of degeneration seen in parkinson disease
midbrain/brainstem
type of degeneration seen in progressive supranuclear palsy
midbrain/brainstem
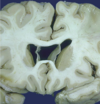
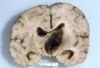
type of degeneration seen in huntington disease
caudate nucleus
type of degeneration seen in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
motor neurons
chromosome associated with beta-amyloid precursor protein in Alzheimer’s disease
21
(alzheimer’s increased in Down syndrome)
gene associated with presenilin 1, associated with Alzheimer’s
14q24.3
gene associated with presenilin 2, associated with Alzheimer’s
1q31-q42
gene associated with tau, associated with Alzheimer’s
17q21.1
____ plaques as seen in alzheimer’s

amyloid
____ ____ of Tau protein as seen in alzheimer’s disease

neurofibrillary tangles
Superficial cortical dark spots denote ____ deposition in Alzheimer’s

hemosiderin
Parkinson’s disease involves the deposition of ____ inclusions (Lewy bodies) with progressive loss of neurons, visible grossly in the substantia nigra.

synuclein
Parkinson’s disease involves the deposition of synuclein inclusions, called ______ _____, with progressive loss of neurons, visible grossly in the substantia nigra.

Lewy bodies
Parkinson’s disease involves the deposition of synuclein inclusions (Lewy bodies) with progressive loss of neurons, visible grossly in the ____ ____.
substantia nigra
Huntington chorea involves chromosome ___, which codifies Huntingtin, containing a polyglutamine sequence due to CAG repeats. Repeats increase with each subsequent generation, increasing the severity of the disease.
4p
Huntington chorea involves chromosome 4p, which codifies Huntingtin, containing a polyglutamine sequence due to CAG repeats. Repeats increase with each subsequent generation, increasing the severity of the disease. This phenomenon is called ___.
anticipation
Huntington’s disease shows ___ nucleus atrophy and neuronal loss. Causes significant dilation of the lateral ventricles.

caudate