Blood transfusion Flashcards
(42 cards)
Why do we transfuse blood?
- For replacement of blood loss
- Failure of blood production
What differentiates the blood groups?
- Arrise from antigens
- (something that invokes immune response
- Red cell antigens are expressed on the cell surface
- Can provoke antibodies
How can we imagine ABO blood types?
Donuts and Sprinkles

What does ABO gene encode for?
Glycosyltransferase
These establish linkages: Glycans added to proteins or lipids on Red Cells
What do A and B genes code for?
Code for transferase enzymes:
- A antigen is N-acetyl-galactosamine
- B antigen is galactose
What does O code for?
- ‘O’ gene is non-functional allele
- So A and B are (co-)dominant and O is recessive
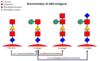
Which blood groups have antibodies against each other?
- If blood group A, have antibodies against B
- If blood group B, have antibodies against A
- If blood group O, have antibodies against A and B
- If blood group AB, have no antibodies against A and B
What does IgM do?
- anti-A/B naturally occurring
Percentage of different blood groups?
- A 42%
- B 9%
- AB 3%
- O 46%
Which red cell vs FFP (fresh frozen plasma) blood groups can be administered to others?
Please see table:

What is RhD?
Either Rhesus negative or positive

What is notable about anti-RhD?
-
RhD negative individuals can make anti-D if exposed to RhD+ cells
- Transfusion or pregnancy
- Anti-D can cause transfusion reactions or haemolytic disease of the newborn
What do we cover for blood donors?
- Extensive ‘behavioural’ screening
- Sex, age, travel, tattoos…………
- Tested for ABO and Rh blood groups
- Screened for HepB/C/E, HIV, syphilis
- Variably screened for:
- HTLV1, malaria, West Nile virus, Zika virus…
What are the components of blood?
- Plasma (clotting, coagulation factors, albumin, antibodies)
- Buffy coat (Platelets, white cells)
- RBCs

What are 4 common indications for red cell transfusion?
- To correct severe acute anaemia, which might otherwise cause organ damage
- To improve quality of life in patient with otherwise uncorrectable anaemia
- To prepare a patient for surgery or speed up recovery
- To reverse damage caused by patient’s own red cells - Sickle Cell Disease
RBC
How do we store?
How long do we transfuse over?
Increments?
- Stored at 4 degrees
- Transfuse over 2-4hrs
- 1 unit increments ~5 g/L
Platelets
Store?
Increments?
Transfuse over?
- Stored at 22 degrees, shelf life of 7 days
- 1 dose platelets (=4 pooled or 1 apheresis donor)
- increments 20-40.109/L
- 20-30mins transfusion
Platelets: What do we do for….?
Massive haemorrhage
Bone marrow failure
Surgery prophylaxis
Cardiopulmonary bypass
- Massive haemorrhage
- Keep platelet count above 75x109/l
- Bone marrow failure
- platelet count <10-15 × 109/litre
- or <20 × 109/litre if additional risk, e.g. sepsis
- Prophylaxis for surgery
- Minor procedures 50x109/l;
- More major surgery 80x109/l; CNS or eye surgery 100x109/l
- Cardiopulmonary bypass
- use only if bleeding
Fresh Frozen Plasma
How many units from?
How do we store?
Indications for use?
Lab test?
- 1 unit from 1 unit of blood
- Store frozen, allowing 30 mins to thaw
- Massive haemorrhage, DIC with bleeding or prophylaxis
- PT and APTT
Cryoprecipitate
How many pools?
Store?
Lab test?
- 1-2 pools if fib <1.0g/dl (1.5g/dl)
- Frozen, allow 20 mins to thaw
- Fibrinogen
How does practical blood banking actually work?
- Blood sent to Blood Bank
- ‘Second sample’ now implemented
- Group and Screen/Save
- Cross match
- Tariff defined by ’MSBOS’
- Samples kept for 7 days
- But only valid for 2 days if recent transfusion
What are the main causes of near miss incidents?
98.9% poor practice, shocking
What is checked for in “group and screening”?
- ABO and RhD type
- Checked against historical records
- Screen for allo-antibodies in serum
Please explain Coombs test:
(AKA antiglobulin test or AGT) is either of two clinical blood tests used in immunohematologyand immunology.
The two Coombs tests are the direct Coombs test (DCT, aka direct antiglobulin test or DAT), and the indirect Coombs test (aka indirect antiglobulin test or IAT)



