Myeloma Flashcards
(24 cards)
What are antibodies?
Are they soluble?
- Produced by B cells, mostly plasma cells
- Primary role is to recognise and bind to pathogens
- Either soluble or membrane bound
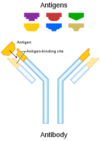
What is the basic structure of antibodies?
- Basic structure - Y –shaped
- 2 heavy chains
- 2 light chains

What are the variable domains of antibodies?
- There are variable domains
- Everything else remains constant
What are the types of heavy chain of antibodies?
- 5 types of heavy chain
- Gamma – IgG
- Alpha – IgA
- Mu – IgM
- Delta – IgD
- Epsilon - IgE
What are the characteristics of each heavy chain?
- IgM
- Initial phase of antibody production
- Exists as a pentamer – highest molecular weight
- IgG
- Most prevalent antibody subclass (75% of total)
- IgA
- Mucous membrane immunity
- IgE
- Parasite immune responses, hypersensitivity
What are the light chains?
- Kappa or lambda
- Random selection for each cell
- But, each cell will only make 1 type of light chain with 1 specificity
- Free light chains are also found in the blood at low levels – difficult to measure
What is the FAB vs FC region of antibody?
- FAB region: variable, defines target binding
- FC region: constant, defines subclass

What are the rough levels of the different types of immunoglobulin?
- IgG : 6-15g/l
- IgA : 1-4.5g/l
- IgM : 0.5-2.0g/l
What is a paraprotein?
- monoclonal immunoglobulin present in blood or urine
- If present, it tells us that there is monoclonal proliferation of a B lymphocyte / plasma cell somewhere in the body
What use is serum protein electropheresis?
- Separates protein based on size and charge
- Forms a characteristic pattern of bands of different widths and intensities based on proteins presenta
What does total immunoglobin levels measure?
What does electrophoresis measure?
What does immunofixation tell us?
What will light chains tell us?
- Total immunoglobulin levels
- Measures Ig subclasses by heavy chain/ Fc section
- Electrophoresis
- Assesses antibody diversity, identifies paraprotein
- Immunofixation
- Identifies what class of paraprotein is present (i.e. IgG, IgM)
- Light chains
- Assesses imbalance/ excess of light chains in urine / serum
Which diseases present with IgM paraproteins?
= Lymphoma
- Maturing B-lymphocytes make IgM antibody at the start of the immune response
Which diseases present with IgG, IgA paraproteins?
= Myeloma
- Mature plasma cells generate these types of immunoglobulin after isotype switching
What is myeloma?
- Neoplastic disorder of plasma cells, resulting (usually) in excessive production of a single type of immunoglobulin (paraprotein)
- Peaks in 7th decade
- Ethnicity – commoner in black population than white
What are the features of myeloma?
- Bone disease
- lytic bone lesions
- pathological fractures
- cord compression
- hypercalcaemia
- Bone marrow failure esp. anaemia
- Infections
What are the effects of IgG and IgA paraproteins in Myeloma?
- Renal failure (cast nephropathy)
- Hyperviscosity
- Hypogammaglobulinaemia
- Amyloidosis
Effects of IgG and IgA paraproteins in Myeloma
Explain the reason for renal failure:
- Immunoglobulin deposition and blockage of renal tubules
Effects of IgG and IgA paraproteins in Myeloma
Reason for hyperviscosity?
- Syndrome caused by increased viscosity in blood, impaired microciculartion and hypoperfusion
- Commonest clinical feature is bleeding – retinal, oral, nasal, cutaneous
- Can also cause cardiac failure, pulmonary congestion, confusion, renal failure
Effects of IgG and IgA paraproteins in Myeloma
Reason for the Hypogammaglobulinaemia?
- Impaired production of normal Immunoglobulin
- Tendency to infection
Effects of IgG and IgA paraproteins in Myeloma
Reason for the amyloidosis?
- Group of diseases characterised by deposition of fibrillar protein
- Morphological appearances, physical structure are similar
- Biochemical or protein composition can vary
-
When caused by a paraprotein or light chains – AL amyloid
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Cardiac failure (LVH)
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Autonomic neuropathy
- Cutaneous infiltration
How do we make a diagnosis of myeloma?
- Paraproteins are common
- 3-4% of population over age of 75
- The vast majority have nothing wrong with them
- This is termed monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance (MGUS)
- Myeloma is diagnosed by finding excess plasma cells in the bone marrow
- Must comprise > 10% of total bone marrow cell population
Which types of paraprotein are present in myeloma?
How do we stage myeloma?
Type of paraprotein
- IgG 55%
- IgA 21%
- Light chain only 22%
- Other (IgD, non-secretory) 2%
Stage
- Based on albumin & beta-2 microglobulin
What are the treatment options for myeloma?
- Chemotherapy
- Proteasome inhibitors, IMiDs, monoclonal antibodies
- Bisphosphonate therapy
- Zoledronic acid
- Radiotherapy
- Steroids
- Surgery
- Pinning of long bones; decompression of spinal cord
- Autologous stem cell transplant
What about IgM paraproteins??
IgM paraprotein Myeloma doesn’t exist
- IgM paraproteins are associated with low-grade lymphomas (various types)
- Clinical presentation
- Bone marrow failure (anaemia, thrombocytopenia)
- Lymphadenopathy
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- B symptoms
- Paraprotein-related symptoms can occur
- Bone disease is very rare


